Fertilization : In the process of intercourse, sperm from semen comes in contact with ovum and fertilizes it. After fertilization embryo is formed. It needs proper nutrition and proper care so that the child is normal after growth.
Embryonic Nutrition : After the development of an embryo the number of cells increases and the developing embryo requires energy for its metabolic activities. The embryonic nutrition deals with the supply of nutrients to the embryo. The nutrition is supplied either through the reserved food material e.g. yolk in the embryo of chick or from the mother directly to embryo.
Embryonic Nutrition in the egg : In the oviparous animals i.e. fishes, amphibians, reptiles and birds, the food required for development is stored in the egg. If the supply is partly stored, the rest of it can be obtained from the environment in which they are developing. Oxygen is always absorbed from atmosphere.
The yolk is made up of proteins, phospholipids and some fats.
On the basis of percentage of these substances, the yolks have been divided into two types.
(a) Protein yolk : If the yolk is having mainly proteins along with a small amount of lipids, it is known as protein yolk. This is mainly found in many invertebrates and in lower chordates.
(b) Fatty yolk : If the yolk is having phospholipids and fats, it is known as fatty yolk. Utilisation of the yolk : There occurs the utilisation of yolk in different manners in different developments. For example,
(a) In mesolecithal holoblastic eggs, (e.g., frog), the mechanism of yolk utilisation is quite simple. When cells undergo divisions the yolk gets distributed mechanically into daughter cells. In them, the yolk is converted into simpler substances by enzymes which are then used to synthesise more protoplasm.
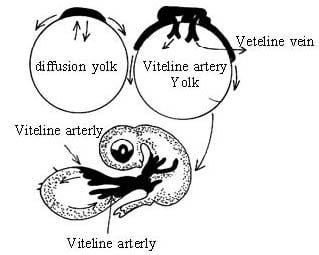
(b) In macrolecithal eggs (e.g., birds) there occurs meroblastic cleavage. During this, the yolk remains outside and during early stages of development, the embryo gets the nourishment by diffusion. However, at a later stage, a yolk sac gets developed around the yolk mass from mesoderm and endoderm. The vitalline vein and artery are formed which connect this sac with the heart. The enzymes convert yolk into soluble form and the vitelline arteries and veins distribute to it all parts of the embryo.
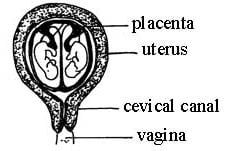
The placenta is defined as an organ formed from some parts of the foetus and some from the uterine wall of the mother for exchange of materials (nutrition and excretion) between the mother and foetus.
Structure : The simplest type of placenta is called epthelio-chorial placenta. The foetal blood is separated from maternal blood by six wall. Three walls belong to foetus and three walls to uterus of the mother. The three walls belonging to the uterus of the mother are as follows:
(i) Mucous epithelium of the uterine wall
(ii) Uterine connective tissue and
(iii) Maternal blood capillaries (maternal endothelium).
Foetal components of placenta are as follows :
(i) Foetal choronic epithelium.
(ii) Foetal connective tissue and
(iii) Foetal blood capillaries (foetal endothelium).
The various nutrients and gases pass from mother to foetus through these six walls.
It is interesting to note that the placenta becomes more effective with the decrease of placenta layers. For instance, three-layer human placenta is 250 times more effective to Na+ as compared to five layered cow placenta.
Physiology of Placenta
(a) Nutrition : The various nutritive substances like glucose, fructose, amino acids, lipids, salts, vitamins and water get transported from the mother’s body to the foetus through the placenta.
(b) Excretion : The nitrogenous wastes like urea and uric acid resulting from metabolic activities in the embryo are passed back through the placenta to be removed through the mother’s excretory systems.
(c) Gaseous exchange : Oxygen passes from mother to foetus through the placenta and carbon dioxide from foetus to the mother, again-through the placenta.
(d) Hormonal : Placenta produces choronic gonadotropins which help in maintaining pregnancy. A hormone relaxin from placenta facilitates birth.
Energy sources of the embryo : In the development of the embryo, growth is due to increase in the amount to protoplasm and in the number of cells.
The source of energy for the embryo is the oxidation of carbohydrates and fats stored in the egg during oogenesis. In the case of embryo developing in the womb of the mother the energy is supplied by the mother. The enzymes required for these oxidation reactions are present in the egg. During most of the developmental period, the energy required is mainly supplied by carbohydrates. However, the fats are used as the sources of energy near the hatching time.
Implantation : After fertilisation, the egg undergoes cleavage to form blastocyst. Then, it moves into uterus or womb where it gets connected with or embedded in the thickened wall of the uterus or the womb. This is known as implantation. After implantation, the embryo develops placenta through which it gets its nutrition from the mother.
Importance of the health of mother during pregnancy
Proper care of mother during pregnancy is of vital importance because the developing foetus gets all its nutrition from the mother and removes all the wastes back into the mother. Hence the mother is acting as the stomach, the liver, the lungs and the kidneys for the foetus. Thus, the mother needs nourishment not only for herself but also for building the baby within her.
(i) If the mother’s nutrition is poor, then the embryo starts taking its nutrition from the breaking up of the maternal tissue. Due to this mother gets weakened in the process.
(ii) Embryo gets vitamins A, B, C, D and E from the mother. The deficiencies of these vitamins in the pregnant mother’s diet may cause a variety of deformations and deficiencies in the growing foetus.
(iii) If enough calcium is not present in mother’s diet, the skeleton may remain fragile.
(iv) Embryo needs glucose for energy which is supplied by the mother. If the diet of pregnant mother contains low content of glucose, then the metabolic activity of the embryo is reduced.
If the mother’s diet contains excess of glucose, the large excess amount of sugar is converted into fat which is then deposited in the body of foetus, causing abnormalities of various kinds.
If the mother is diabetic, then the embryo may also be affected by the disease.
(v) The barriers in the placenta are selective in nature and they do not permit the entry of harmful substances into the embryo. However, certain drugs (e.g. thalidomide) and antibodies against Rh factor as well as virus measles and syphilis bacteria may pass through barriers, thereby affecting the developing embryo.
One should take proper care of the mother throughout the pregnancy period and especially during the later half of the pregnancy.
Abnormalities : The areas dealing with embryonic abnormalities is called teretology.
Conjointed twins : These are the abnormal twins which are fused with each other, wholly or in part.
Monozygotic twins : These are the twins which are developed from the same zygote.
Dozugotic twins : These are the twins which are developed from two different zygotes.
Free martin : It is a male-like female which remains sterile. This is due to the impairing of sexual development of the female foetus.
Mongolism : Sometimes children born to the mother of over 40 years of age are both physically and functionally idiots called Mongoloids. Out of 700 births, only one is found to be a mongol.
Idiots exhibiting mongolism have a broad forehead, permanently open mouth with tongue projecting outwardly with deficient mental level.
The defect arises due to a change in the number of chromosomes in the germ cell. In these is a failure of the separation of twenty first pair of chromosomes during meiosis and this causes the formation of an egg having 24 chromosomes instead of 23. If such an egg gets fertilised, the resulting zygote would give rise to mongoloid.

2. Multiple births : Normally, a woman gives birth to a single child. But sometimes she gives birth to more than one child at a time. This is called a multiple birth.
In multiple births, the numbers of births is 2 and the children thus born together are called twins. But sometimes the numbers may be 3 (triplets), 4 (quadruplets), 5 (quintaplets) or even more. It is interesting to note that as many as 11 children have been born at a time.
3. Inborn errors of metabolism : The defects arising due to gene mutations are known as inborn errors of metabolism. An interesting example of inborn errors of metabolism is phenylketonuria. In this condition the embryo does not utilise protein food properly which results in the accumulation of amino acid, phenylalanine and some of its derivates to the toxic level. This causes retardation of growth and brain development. It is interesting to report that this defect can be detected early and by supplying a regulated diet the individual can be made to lead a normal life.
Abnormalities in development may occur due to genetic cause, damaging external agents or malnutrition. The six out of a number of birth defects during embryogenesis are as follows:
(a) Mongolism : In this defect the individuals born are both physically and functionally idiots. This defect arises due to chromosomal error.
(b) Achondroplasia : It is a hereditary (genetic) developmental defect in which the right half body is normal whereas the left half is like that of a dwarf.
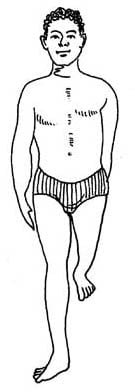
(c) Moromelia : This is a hereditary (genetic) abnormality of development in which the born is having peg-like limbs without hands and limbs. In this figure, a father and his son are shown. The mother was normal.

(d) Club feet : It is a hereditary (gen-etic) abnormality during development. This results in inward bending of feet.

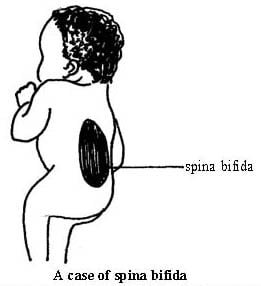
(e) Spina bifida : It is a developmental defect which is caused by the mother being infected with German measles during pregnancy.
(f) Phocomalia : In this defect, there is no development of long bones or limbs and hands and feet are attached directly to the trunk. This defect has been caused by taking the heavy doses of thalidomide in early stages of pregnancy.
X-ray Exposure : A pregnant woman should avoid exposure to X-rays or other radiations because it causes many defects in the germ cells of the foetus. The defects may be one of the two types.
(a) Direct defects : The radiation may cause a direct damage of the parts of the foetus which may be similar to the defects produced by disease germs, chemicals or drugs.
(b) Indirect defects : The radiation may affect the germ cells in such a way that these defects are expressed after many generations.
Hence a pregnant woman should avoid exposure to X-rays.
(ii) Pregnant woman should be careful in taking drugs
Some drugs have harmful effects on the foetus. Hence such drugs should be totally avoided. A drug called thalidomide given to the pregnant woman to reduce vomiting has resulted in the birth of thousands of children without arms or legs. Many other drugs like quinine busulphan chlorambucil and aminopeterin are also harmful for the foetus. Hence to avoid any complication a pregnant woman should be very careful in taking drugs.
(iii) The diet of pregnant woman should not be deficient in vitamins A, B and D
The diet of a pregnant woman should be rich in vitamins A, B and D. If the pregnant females are given food deficient in vitamins A, B and D, they may produce very defective offspring. These defects include hare lip, cleft plate spina bifide, skeletal defects of a long bones, vertebral column and skull, eye defects and brain defect. Hence the diet of pregnant woman should not be deficient in vitamins A, B and D.
Causes of developmental abnormalities : The following are the main causes of developmental abnormalities during embryogenesis.
(i) Abnormalities due to genetic causes.
(ii) Abnormalities due to external damaging agents.
(iii) Abnormalities due to malnutrition.
(i) Abnormalities due to genetic causes : The abnormalities may be due to any of of the two causes.
(a) Chromosomal errors : These defects are caused due to the increase or decrease in the number of the chromosomes in the somatic or germ cells. If the defects occur in somatic or germ cells, they affect only some parts of the embryo and the defects is not inheritable. But the defects of the germ cells are inheritable. Mongolism is its example. These individuals are born idiots.
(b) Gene mutation : Many defects are caused by gene mutations in the germ cells also. In the individuals. For example colour blindness, hare lip, foot holes in the heart etc.
(ii) Abnormalities due to external damaging agents : The following are the external damaging agents which cause defects in the embryo.
(a) Disease producing organism : If a pregnant woman gets an attack of German measles the child may have several defects such as blindness, defective heart, hare lip, spin, bifida. Syphus germs cause still birth or congenital abnormalities.
(b) Chemical substances : Several chemicals like aminopterin and antifolic acid cause abnormalities. Vitamin ‘A’ if given in excess causes defects including hydrocephalus spina, bifida, ectromelia and phocomelia. Mercury causes cerebral palsy.
(c) Various drugs : Various drugs taken by the pregnant mother during the first twelve weeks of their pregnancy cause a great harm to the foetus e.g. guinine chloroambucil, aminopterin.
(d) X-rays and other radiations : X-rays and other radiations are very harmful and cause many developmental abnormalities. Many abnormalities are represented after many generations. These are called indirect effects of radiations. Sometimes radiations have direct effect on the foetus harming different parts of the body.
(iii) Abnormalities due to malnutrition : The embryo gets its food from the mother. If the mother does not get a good diet then the development of embryo is abnormal. These defects include hare lip, cleft palate, spina bifida, skeletal defects of long bones etc.
(i) Identical twins : The twins which are of the same sex and are identical in all respects including appearance, height and behaviour are called identical twins.
Development of identical twins : The identical twins are monozygotic which means that they develop from the same zygote. The zygote undergoes cleavage to form a blastocyst. The blastocyst divides into two embryonic masses due to unknown reasons. Each embryonic mass gets attached with the same placenta separately. The two parts develop into complete body separately.

(ii) Fraternal Twins : These twins may be of the same sex or different sex; they may or may not resemble each other; such twins are called fraternal twins. Development of fraternal twins : These twins are dizygotic. They develop from two different zygotes. Sometimes a woman produces two ova which are fertilized independently and develop separately into two individuals called fraternal twins.

(i) Conjoined twins : Twins are produced either from one zygote or two zygotes. Generally the twins develop completely normal in shape and all other respects. But sometimes the twins fuse partly or wholly. Such twins are called conjoined twins. Such twins do not survive for long.
(ii) Free murtins : In dizygotic twins there are two separately placentae. Sometimes these two placentae fuse with each other. As a result of this a blood vascular connection is established between the two developing fetuses. If the twins are of male and female type then the blood of the male foetus mixes with the blood of the female foetus. This prevents the development of female sex organs in the female foetus. The female foetus becomes male like and becomes sterile. This female is called free murtin.

