Viruses : Viruses are very minute, acellular and ultramicroscopic particles consisting of one or more molecules of either DNA or RNA but not both, enclosed in a coat of protein.
Viruses can live and multiply only in the host cells.
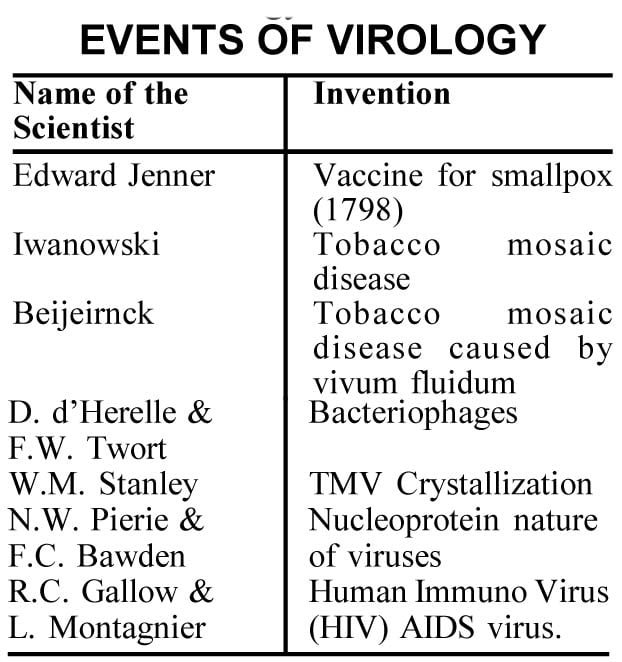
Virology : The branch of science which deals with the study of viruses is called virology.
Types of Viruses
Plant viruses of Phytophages : These viruses mainly infect the plants.
Animal viruses of Zoophages : They attack various animals.
Bacteriophages : The viruses that attack bacteria are called bacteriophages.
Mycophages : These viruses attack the fungi.
Zymophages : Zymophages infect the yeast cells.
Cyanophages : These viruses attack the blue green algae (cyanobacteria).
Vertebrate viruses : They infect vertebrates only.
Invertebrate viruses : They infect invertebrates.
Structure of viruses
Size : Virus particles are called ‘virions’. Virions or viruses range in size from about 10 to 300 nm diameter.
Shape
Rod shaped, e.g. Tobacco mosaic virus
Rectangular, e.g. Vaccinia virus
Polyhedral, e.g. Adenovirus
Spheroidal, e.g. Polio virus
Tadpole shaped, e.g. Bacterio-phages
Bullet shaped, e.g. Rhabdovirus
Symmetry
Helical symmetry : e.g. Tobacco mosaic virus.
Cubic Symmetry : e.g. Adenovirus
T2 and T4 (T-even) bacteriophages exhibit a form which is a combination of two symmetries above.
Chemical Structure
Most viruses have an outer protein shell (capsid) and the enclosed nucleic acid (core). Both together are referred to as the ‘nucleocapsid’. Viruses consist of either DNA or RNA.
Replication of viruses : Replication is the process of multiplication in viruses.
Plant Diseases caused by Viruses
Vertebrate viruses : They infect vertebrates only.
Bacteriophage : The viruses that infect bacteria are called bacteriophages.
Plant Diseases : 1. Tobacco mosaic : Chlorosis leading to mosaic appearance of leaf; leaf curling and mottling, caused by Tobacco mosaic virus. Colour change is the main thing.
2. Rice tungro : Leaves turn yellow from the tip downwards; plant shows stunted growth and bears empty grains.
3. Banana bunchy top : Stunted growth, leaves develop into a dense rosette like structure at the apex; marginal chlorosis and leaf curling, caused by Banana virus I.
4. Sugarcane Mosaic : Sugarcane mosaic virus makes pale patches on leaves.
5. Bhindi yellow vein mosaic : Vein clearing followed by chlorosis; fruits dwarf and malformed.
6. Apple mosaic : Yellowish patches on the leaf leading to necrosis.
7. Potato leaf roll : Characteristic rolling of leaves which become leathery. Caused by Potato virus 1, Solanum virus or leaf roll virus.
8. Papaya leaf curl : Curling of leaves. Caused by Tobacco virus-16 or Nicotiana virus-1.
9. Tomato leaf curl : Stunted growth, Dropping and curling of leaves. Caused by Tobacco virus-16 or Nicotiana virus-0.
10. Potato rugose mosaic : Dwarfing of plant, mottling of leaves; leaves become rugose, rough and hairy. Two viruses known as potato virus-X and potato virus-Y jointly cause the disease.
11. Cucurbits mosaic : Mottling of leaves with dark-green, light-green or yellow-green patches; fruiting reduced.
12. Tomato bunchy top : Stunted growth leading to bushy appearance.
13. Tulip mosaic : Variegation of flower petals.
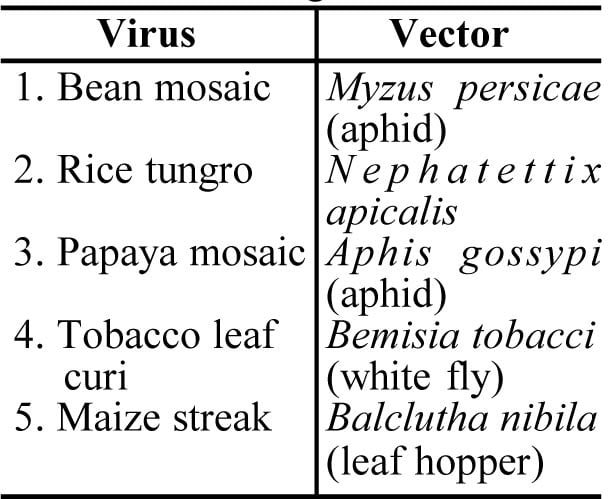
Transmission of Plant Viruses : Some of the plant viruses and their insect vectors are given below—
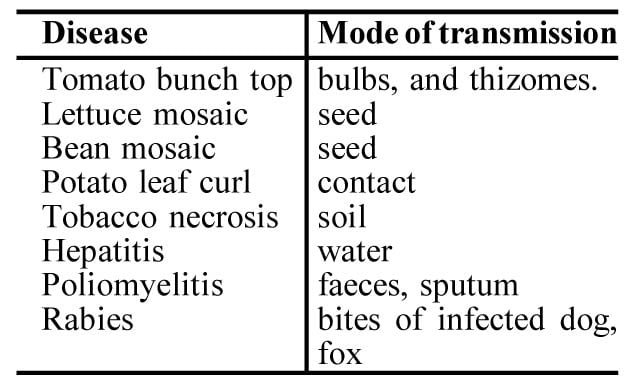
Some of the viral diseases are transmitted through other means not involving vectors.
Air borne transmission : Viral diseases of respiratory infections are transmitted through air. Small pox, polio-myelitis, influenza viruses, etc. are transmitted through air.
Transmission through contact : Direct or indirect contacts is the chief cause of transmission of viral diseases in crop plants. For example, potato virus-X spreads in the whole field through contact between diseased and healthy plants during strong wind.
Hereditary transmission : Transmission takes place in animal viruses through the eggs of the infected parents. Such diseases are small pox, chicken pox and rift valley fever.
Some of the viral diseases transmitted through other means without involvement of vectors.
Prevention and Control of Plant Viral diseases
Isolation of source of infection: This prevents the entry of the source of infection in the area where it does not exist.
Isolating the source of infection.
Eradication of vector : Complete eradication is achieved by using suitable insecticides.
Cultivating the disease resistant varieties.
Chemotherapy : Plant viral diseases are eradicated by giving chemical treatment.
Other modes of Transmission of viral diseases—
(a) vegetative parts
(b) mechanical transmission
(c) pollen grains
(d) insects
(e) nematodes
(f) fungi
(g) body fluids.
Heat therapy : Viruses causing infection in plants are destroyed by giving heat treatment at higher temperture about 55OC.
Phycophage : Virus attacking algae.
Cyanophage : Virus attacking blue-green algae.
Mycophage : Virus attacking fungi.
Zymophage : Virus attacking yeast.
Eclipse Phage : Replication of phase DNA and direct synthesis of new capsid components.
Coliphage : Virus attacking E. coli bacteria.
Arbovirus : Viruses transfered by insects from one host to another transmitted sexually or through blood.
Interferon : Antiviral substance produced by infected cell.
Lysis : Breakdown of bacterial cell wall releasing viral particles.
Lysozyme : Enzyme produced by a bacteriophage to make a hole in the bacterial cell wall to facilitate entry of viral genome.
Viroid : Extremely simple infectious agent, having only small RNA genome without protein coat.
Prions : Proteins without nucleic acid which can multiply themselves and are infectious.
Virion : These are virus particle capable of causing infection.
AIDS : Viral disease in human being transfusion caused HTLY-III (Acquired Immuno Deficiency Syndrome).
Capsomere : Identical protein subunit of capsid in virus.
Capsid : Viral protein coat surrounding the nucleic acid.
Peplomeres : Lipoproteinaceous structural units of envelope surrounding the virus.

