Respiration : Respiration is the process which involves the oxidation of food substances in the body to release energy. It is very important process.
In respiration, there occurs exchange of gases, oxygen and carbon dioxide, between the body and the outside environment.
Respiratory System : The various organs required for gaseous exchanges are said to form a respiratory system.
Various organs of respiratory system are:—
Nasal, nesopharynx, larynex, trachea, bronchi, lungs.
Inspiration : It is the process which involves breathing in oxygen rich air.

Expiration : It involves breathing out of air loaded with carbondioxide.
Approximate Composition of inspired and expired air
Inspired Air Expired Air
Nitrogen 79% 79%
Oxygen 21% 16%
Carbon dioxide 0.04% 4%
Water vapour variable sufficient
Residual Volume : It is the volume of air which remains in the lungs after maximum forceful exhalation.
About 1.5 litres of air is left behind in the respiratory system.
Tidal volume : It is the amount of air which moves in the respiratory passage during each inspiration or the amount of air which moves out with each expiration.
It is about 500ml in an adult.
Vital Capacity : It is about 3.5 to 4.5 litres in normal adult person. It is the maximum amount of air that can be expired after maximum inspiratory effect.
Inspiratory Reserve Volume (IRV): It is the additional volume of air that can be breathed with maximum forceful inspiration by a person.
A person can inspire 2-3 litres of air in excess of his tidal volume.
Expiratory reserve volume : It is the additional volume of air that can be breathed out with maximum effort by a person after breathing out his tidal volume. A person can breathe out additional volume of about 1 litre of air.
Vocal Cords : These are the folds of mucous membrane stretching across the lumen of larynx. They are known as vocal cords. They vibrate when air is blown through the larynx. This produces voice.
The passage of air is as follows:—
Nose—Pharynx—Trachea—Bronchi
Alveolus—Bronchioles
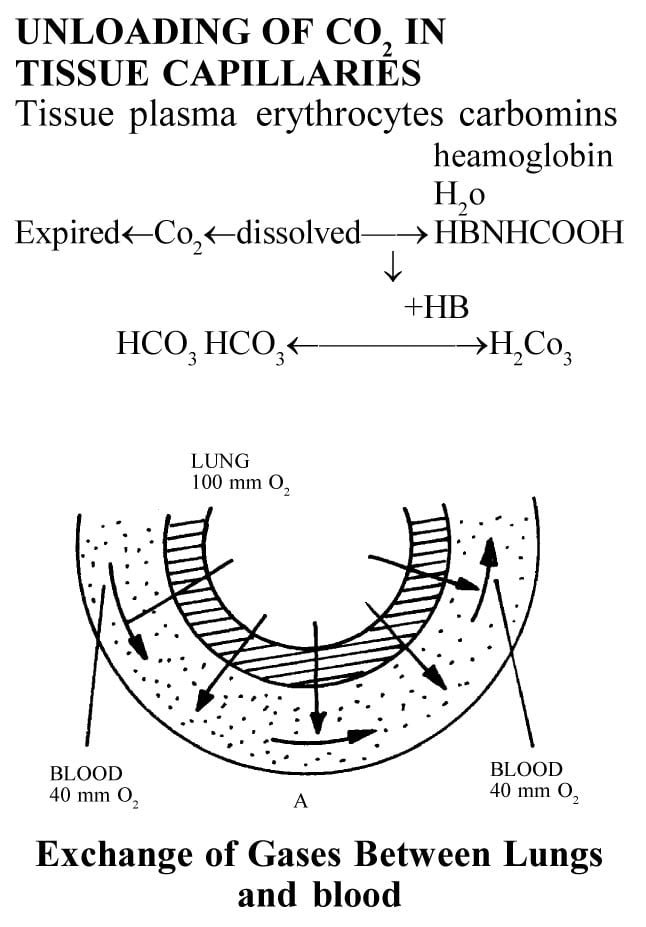
Various steps of gaseous exchange in the lungs
(i) Exchange of air between the atmosphere and alveoli.
(ii) Exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide between alveolar air and lung capillaries by diffusion.
(iii) Exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide between blood and tissues of body by diffusion.
In the lungs oxygen is loaded and carbon dioxide is unloaded from the blood.

Total Lung Capacity : It is the volume of air in lungs and respiratory passage after a maximal inhalation effort. It is equivalent to vital capacity plus residual volume. It is about 5000 to 6000 ml in adult males.


Hypoxia or anoxia : It is a disease in which lack of oxygen is produced in the body.
Asphyxiation : Lack of oxygen coupled with increase in carbon dioxide concentration in the body is known as asphyxiation.
Pneumonia : In pneumonia, there occurs the accumulation of lymph and mucus in the alveoli and bronchioles due to bacterial infection.
It is caused by bacterium Diplococcus pneumoniae.
Tuberculosis : It is caused by a gram +ve bacterium ® Mycobacterium tuberculosis.
This bacterium enters the breathing system and grows in lungs. It is an infectious disease which spreads through the sputum of the infected person.
Cough : It is a sudden forcible expiratory act.
Sputum : It is the mucus which is expelled from the trachea via the mouth. The main constituent of sputum is the dust particles which were not filtered out by the nose.
B.C.G. : It is a vaccine which is used to curb tuberculosis. It stands for Bacillo calmette guerin.
Nicotine : It is the main constituent of tobacco and has harmful effects on the nervous system, blood vessels, digestive organs and lungs.
Benzopyroene : It is a compound found in tobacco. It is known to cause lung cancer.
Mountain Sickness : This sickness is caused due to oxygen shortage in the inspired air. It develops only in mountaineers climbing to high altitudes without the aid of oxygen cylinders.
Decompression Sickness : At the bottom of the sea the body of the diver is subjected to high pressure by the surrounding water. Breathing of air increases the partial pressure of gases in alveoli.
Too much nitrogen diffuses into and dissolves in the blood and body fats. It reduces working capacity of a diver and he feels drowsy.
When a diver comes to sea surface the pressure falls and nitrogen comes out of the body of the diver and forms gas bubbles in the blood and tissues. These are called bends. These block pulmonary vessels causing breathing problems. To avoid this situation the diver should be lifted very slowly to sea surface, then nitrogen will come out slowly.

