Excretion : It is the process that eliminates the waste products formed beacause of anabolism and catabolism of the body. Excretion involves the removal of nitrogeneous waste products from the body.
Various waste products :
Ammonia, urea, uric acid, bile pigments, excess salts and water are the waste products.
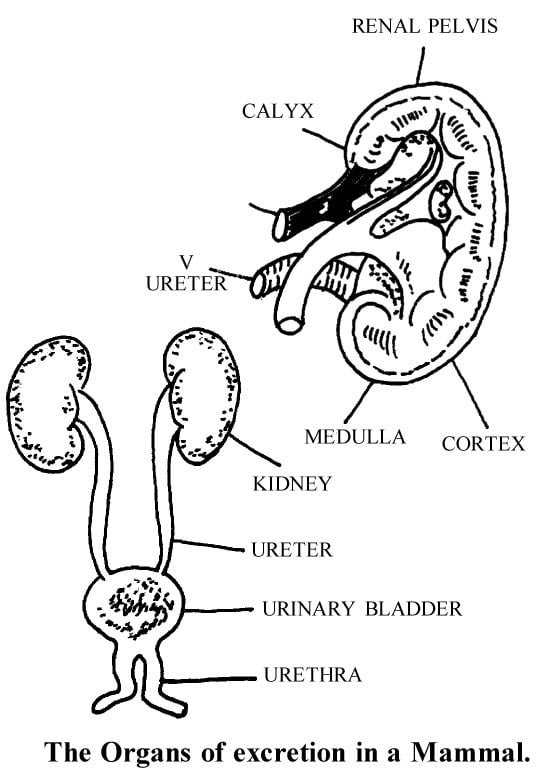
Excretory organs : These are the organs which are concerned with the excretion of waste products. In vertebrates excretory organs are skin, lungs, intestine, kidneys and liver.
Egestion : It refers to the elimination of undigested food formed in the cells or in the lumen of intestine which passes through alimentary canal.
Secretion : It is the production of useful chemical materials by living cells which are utilised in other parts of body.
Ketosis : Ketosis is related to the accumulation of excessive quantity of ‘Ketone bodies’ in the body. The ketone bodies are acetoacetic acid, b-hydroxy-butytric acid and acetone.
Perspiration : It is the process of elimination of wastes through the sweat glands is called perspiration. The excreted matter contains about 99% water.
Micturition : It is the act of voiding the urine.
Osmoregulation : The capability of an organism to regulate the ionic concentrations of the body is known as osmoregulation.
Nephridia : Nephridia are tubular excretory organs of the annelides (earthworm, leaches etc.) which open into the body cavity.
Dialysis : It is the process of separating the large solute particles from small ones using a semipermeable membrane.
Jaundice : When the level of bile pigments increases in the plasma of the blood, the white of the eye and the mucus membrane appear yellow. This condition is known as jaundice. It is due to abnormality of liver.
Nephron or uriniferous tubule : It is the structural and functional unit of kidney.
Hemodialysis : It is a method in which an artificial kidney is used to remove waste products like urea from the body.
Physiology of excretion
In human beings, urine is filtered at + 15 mm of Hg.
(GHP = + 65 mm of Hg)—glomerular hydrostatic pressure
(BCOP= – 32 mm of Hg)—blood plasma colloidal osmotic pressure
(CHP = – 18 mm of Hg)—capsular hydrostatic pressure
Net effective filtration pressure (NEFP) = + 15 mm of Hg
Plasma filtered in 24 hours = 170 liters
Urine filtered in 24 hours = 1.5 litres
The hormone ADH which is secreted by the neurohypophysis of the pituitary gland with the help of osmoreceptor situated in the hypothalamus region regulates the water reabsorption. The secretion of ADH is also controlled by the intake of water. If water intake is less, more is the secretion of ADH which will be affecting more reabsorption of water but process is reversed when water intake is high. Reflex action also controls the urine excretion in infants.
Steps—Three steps are involved in the urine formation—
(1) Ultrafiltration : It is performed in Bowman’s cup of nephron. Net filtration pressure which is about + 15 mm of Hg is responsible for ultrafiltration.
(2) Reabsorption : Useful substan-ces which are filtered under pressure into kidney tubules are reabsorbed by the network of blood vessels around them. After reabsorption the filterate remained is called urine.
(3) Secretion : This is the secretion of remained excretory matter into the kidney tubules from the network of blood vessels surrounding them.
Composition of Urine
Urine consist of organic and inorganic substances. Following are the quantities of different substances in total amount of urine in 24 hours—
(A) Organic substances
1. Urea—25-30 gram
2. Creatine—60-150 gram
3. Creatinine—1.2-1.7 gram
4. Ammonia—9.3-1.0 gram
5. Hippuric acid—0.1-1.0 gram
6. Amino acid—150-250 gram
7. Uric acid—0.5-0.8 gram
8. Oxalic acid—10-30 mg.
9. Vitamins, hormones and enzy-mes—Trace
(B) Inorganic substances
1. N2—25-35 gram
2. Chloride—6-9 gram
3. Phosphate—0.8-1.3 gram
4. Sulphate—0.8-1.3 gram
5. Na—4-5 gram
6. Ca—0.1-0.3 gram
7. K—2.5-3.0 gram
8. I2—50-250 m gram
9. Pb—50 m gram
10. Mg—0.1-0.2 gram
11. As—50 m gram
Urea cycle : Ammonia is released in oxidative deamination in liver.
CH3 = CH3
ï ï
CH-NH3 + ½ O2 ® CO+ NH3COOH
ï ï Ammonia
COOH
Amino acid
This ammonia now undergoes ornithine-arginine cycle and gets changed into urea.

