Enzymes : Enzymes are biocatalysts that accelerate the rate of biological reactions in our body. All reactions in the process of digestion of food are brought about by enzymes. They are similar to catalyst in chemistry in their action.
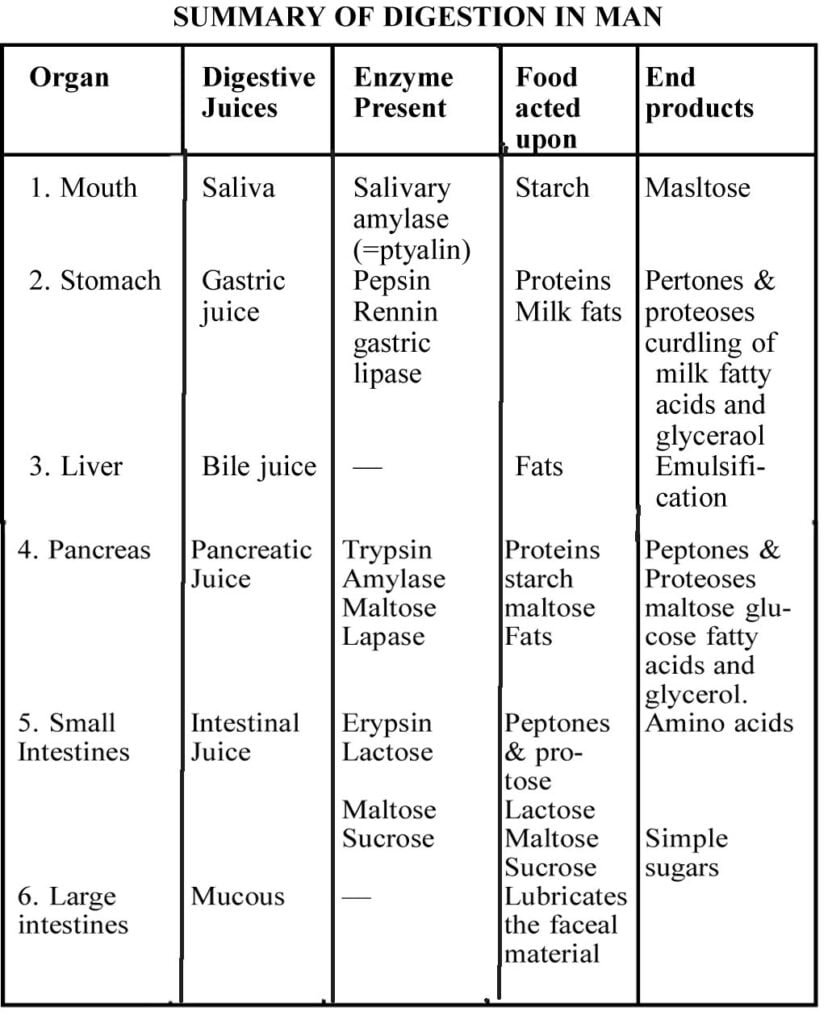
Digestion : It is a hydrolytic process and is carried out by a number of enzymes. Digestion starts from mouth and goes up to the intestines.

Deglutition : Deglutition is the process of swallowing of food from the mouth cavity.
Peristalsis : The involuntary muscle of alimentary canal produces a wave of contractions and relaxations from anterior to posterior end thus pushing the bolus of food. This wave is known as peristaltic wave and the phenomenon is peristalsis.
Jaundice : It is a viral disease of the liver.
Vomiting : It is a reflex process that serves to relieve the upper part of gastro-intestinal tract by forcible expulsion of gastric contents through the mouth.
Emetics : These are substances that cause vomiting such as drinking of sodium chloride, warm water etc.
Ulcers : It is a disease caused by the high concentration of hydrochloric acid in stomach.
Constipation : It is a condition in which the faecal matter passes out of the body (defecation) at prolonged periods.
Diarrhoea : It is a condition in which the food passes down the alimentary canal very fast as a result defecation become very frequent. It is a kind of disease.
Basal Metabolic Rate (BMR) : Even when a person is having complete rest, some amount of energy is spent. This minimum amount of energy spent is known as basal metabolic rate. It is dependent upon size, weight, sex, age, amount of thyroxine in the body, temperature etc.
Balanced diet : A diet having all the essential food constituents in proper proportions is called a balanced diet.
Approximately a balanced diet should have 60% carbohydrates, 25% fats, 15% proteins, minerals and vitamins.
Vitamins : These are important organic compounds present in small amounts in our food, specially vegetables and fruits. They are essential for normal growth and activity of our body. They do not provide energy.
Minerals : Mineral salts are present in small amounts in our food and regulate various metabolic activities in our body.
Important Minerals required for normal functioning of our body
Calcium, phosphours, iron, iodine. In addition to these we need potassium, sodium, mangnesium, maganese, copper, zinc, sulphur, cobalt, fluorine and chlorine.
Protective Fluids : Vitamins and minerals together keep the body free from diseases and are called protective fluids. The deficiency causes several diseases.
Absorption : It is the process by which the digested food particles are taken by the cells of living organism.
Passive absorption : It is the movement of particles from the intestinal lumen into the intestinal cells or blood depending upon the concentration gradient between the two. Passive absorption is a slow process.
Active absorption : The intestinal cells actively take part in absorbing a substance by spending energy. Active absorption can occur even when the concentration of substance is much lower in the intestinal lumen than in blood Sodium, glucose, fractose and amino acids are absorbed by this process.
Calorific value and physiological fuel value of Carbohydrates
Calorific value of carbohydrate
1g = 4.1 k cal
Calorific Value is the energy released by complete oxidation of one gram of carbohydrate in a bomb calorimeter.
Physiological Fuel Value of Carbohydrates : It is the amount of energy produced by 1 g of carbohydrate on oxidation in body.
1g = 4.1 k cal.
Calorific value of fat 1g = 9.45 k cal
Physiological fuel value of fat
1g = 9.0 k cal.

