Nervous system is responsible for complete control and co-ordination of the body and mind.
Co-ordination : For the evolution of multicellular organism, it became absolutely necessary to develop certain system which may co-ordinate the functions among the different cells tissues and organs and may exchange the information between the changes in external environment and internal cellular environment. For this purpose primarily nervous system developed and as the complexity increased another system of co-ordination was also evolved which is now known as endocrine system.
Nervous system : The nervous system is that which receives the stimulus, transmits it to other organs of the body, and the corresponding effects shown is known as nervous system.
Nervous system in man
(1) Central nervous system (CNS) : Brain and spinal cord.
(2) Peripheral nervous system : Nerves from brain (cranial nerves) and spinal cord (spinal nerves).
(3) Autonomic nervous system : Nerves and ganglion coming from the ventral part of the spinal cord.
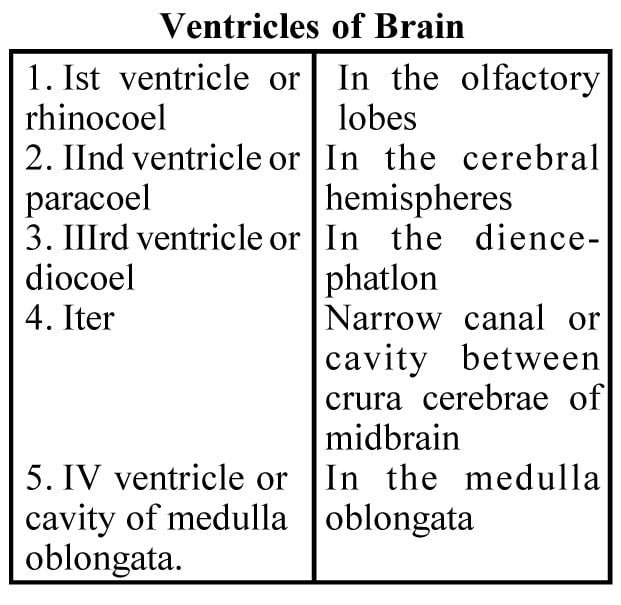
Coverings of nervous system : Brain and spinal cord is covered by membranous meninges. Skull covers the brain. These are from inside to the outside piamater, arachnoid membranes and duramater respectively. The cavities of brain are ventricles, spinal cord is central canal and the cavities present between the meninges are subdural and sub-arachnoid spaces.
Piamater is thin and highly vascular. Cerebrospinal fluid is present in subarachnoid space but not in subdural space.
The Brain
Brain (encephalon) consists of three parts—
(1) Fore brain (prosencephalon) : It includes cerebral hemisphere (telencephalon), olfactory lobe and the diencephalon.
(2) Mid brain (mesencephalon) : It has optic lobes (four lobes) also known as corpora quadrigemina and cerebral peduncle.
(3) Hind brain : It consists of cerebellum (metencephalon) and medulla oblongata (myelencephalon).
Cerebral hemispheres have the folds and grooves respectively known as gyri and sulci. The outer layer of cerebral hemisphere is cerebral cortex and is made up of grey matter which contains the nerve cells in it. Highest centres of sensations and activities such as general sensory, visual, auditory, premotor and motor area etc. are present in grey matter.
Nerve centres for hunger, thirst, temperature control, emotional reactions and the autonomic nervous system are contained in hypothalamus. It also controls the secretion of adenohypophysis (anterior lobes) by the neurohormone secretion. The specialized cells known as nuclei preopticus or preoptic nuclei situated in the hypothalamus are neurosecretory cells secreting the hormones for the storage of posterior pituitary or neurohypophysis.
The optic lobes control muscle tone and modify the signals produced by the cerebral cortex.
The centres for the maintenance of balance, posture and muscle tone are in the cerebellum.
The posteriormost and the last part of the brain is medulla oblongata and pons varolii which have the centres of vital importance such as respiration, salivation and circulation.
Special features :
1. Both the cerebral hemispheres are joined together internally by a strip of nerve fibres called corpus callosum.
2. In the somasthetic area of parietal lobe, the centres for cold heat touch etc. are located.
3. Pons varolii is made up of white N.F. it joins both cerebellum.
4. Brain stem is the end part of medulla.
5. Most of the involuntary activities are controlled by medulla.
6. Sneezing and coughing centres are located in medulla.
Spinal cord : The position of grey and white matter is reversed in the spinal cord to that of the brain i.e. white matter surrounds the grey matter. The spinal nuclei are embedded in the grey matter.
The spinal cord bears central canal. Wing like ridges of grey matter are called dorsolateral and ventrolateral horns respectively. Lateral horns are also found in thoracic and lumbar region.
Dorsal sulcus of spinal cord is joined with central canal by dorsal septum.
Spinal cord is the centre of reflex actions and it forms link between brain and spinal nerves.
The nerve tracts of spinal cord are of two types :
The ascending tract is the sensory tract which transmits the nerve impulses from the peripheral organs to the brain.
The descending tract is the motor tract which sends the nerve impulses from the brain to the muscles and glands.
Peripheral nervous system : The peripheral nervous system is made up of nerves with efferent and afferent nerve fibres. These are motor and sensory fibres. There are 31 pairs of spinal nerves in man and 37 pairs in rabbit. The nerves originated directly from cranium of brain are known as cranial nerves. They are 12 pairs in mammals.
The activities of visceral organs are regulated by nerves and a chain of ganglion which constitute the autonomic nervous system. This system includes two sub-systems :
The sympathetic system : A pair of sympathetic nerves with a chain of ganglions form this system. It starts from the neck and goes to the end of abdomen. These nerves secrete a chemical ‘sympathin’ which accelerates the action of the organ.
The parasympathetic system : The parasympathetic fibres are associated with the nerves of the head and sacral region. These fibres on stimulation secrete the acetylcholine which inhibits the action accelerated by the sympathin.
Spinal nerves
1. Cervical nerves—8 pairs
2. Thoracic nerves—12 pairs
3. Lumbar nerves—5 pairs
4. Sacral nerves—5 pairs
5. Coccygeal nerves—1 pair
All the spinal nerves are mixed. Each develops from dorsal and ventral roots of spinal cord.

