
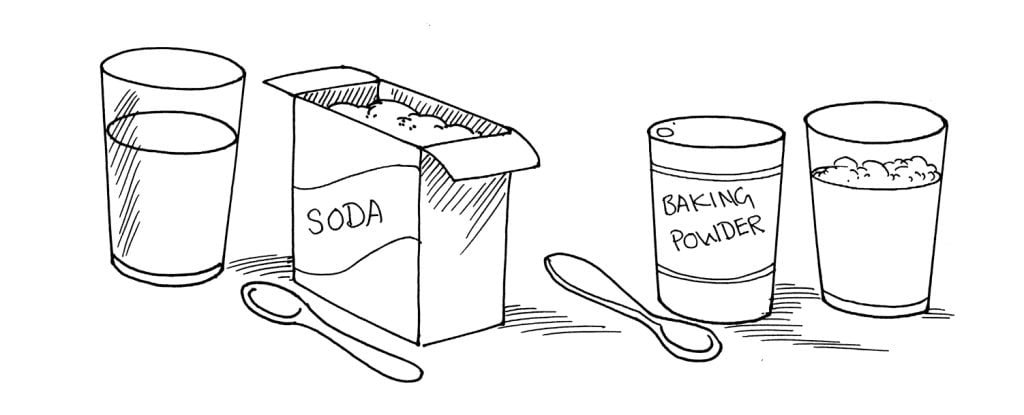
How is baking powder different from baking soda?
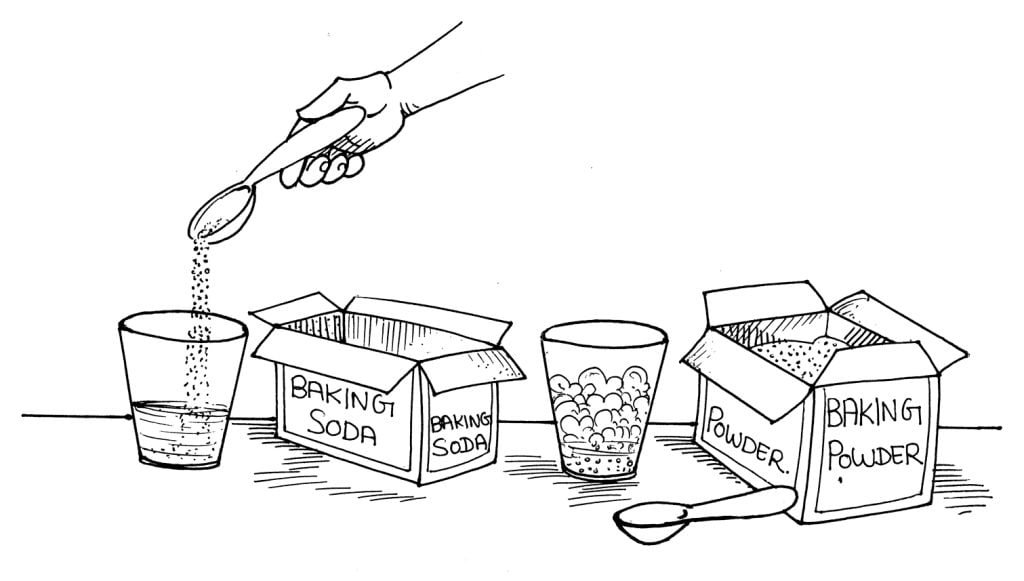
Things Required:
2 glasses of water
1/2 teaspoonful of baking soda
1/2 teaspoonful of baking powder
Directions:
Add the baking powder to one glass of water. Add the baking soda to the other.
This Is What Happens:
The water with the baking powder bubbles. The water with baking soda does not.
Science Behind It:
Baking soda is an alkali, the chemical opposite of an acid. When it combines with an acid, it forms carbon dioxide.
Baking powder is a combination of baking soda and an acid. When you add baking powder to water or milk, the alkali and the acid react with each other and produce carbon dioxide, the bubbles.
There are three types of baking powder. Each one contains baking soda. In addition, they each contain an acid-either cream of tartar (tartrate baking powder), monocalcium phosphate (phosphate baking powder) or a combination of calcium acid phosphate and sodium aluminium sulphate (double-acting baking powder).

