Why do bubbles rise in liquids? This is what we are going to find out.
Things Required:
Large-mouthed jar, 1 gal. (4 litre)
Clear plastic tubing, 20 inches (50 cm)
Small balloon
Directions:
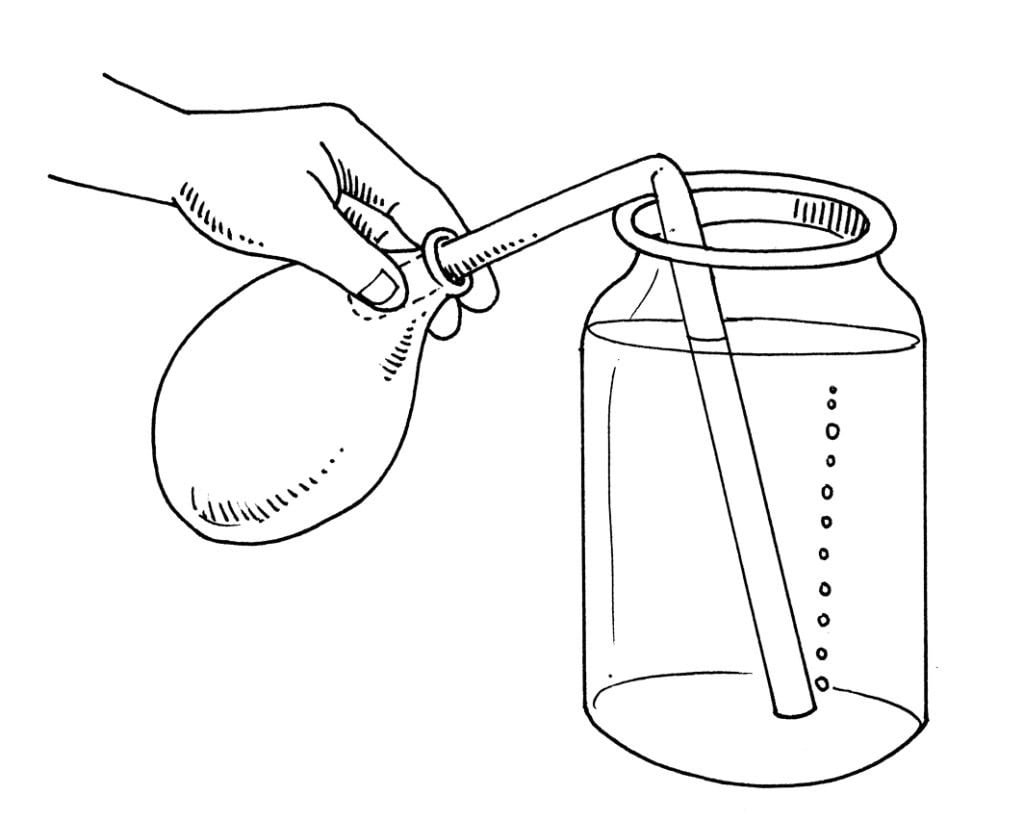
Fill the jar with water. Place one end of the clear plastic tubing in the water at the bottom of the jar. Inflate the balloon and twist the neck to prevent the air from escaping. Slip the mouth of the balloon over the end of the tube. Hold securely with your fingers. Untwist the balloon and allow the air to escape slowly through the tube. Watch the end of the tube in the water and notice the movement of the air as it exits the tube.
This Is What Happens:
Bubbles are formed at the end of the tube. The bubbles rise to the top of the surface of the water and escape into the air.
Science Behind It:
The gas bubbles push water out of their way as they emerge from the end of the aquarium tube. The weight of the water pushed aside equals the amount of upward force on the bubbles. This force is called the buoyancy force. The gas bubbles are so light that they quickly push to the top of the water where they break through the surface of the water and mix with the air surrounding the jug.

