The human body is like a well-organised machine. It is capable of performing different tasks. The human body has a specialised structure, both inside and outside. The body-parts work together to perform several functions in orderly manner.
Cell

The cell is the fundamental structural and functional unit of all living organisms. It is the smallest unit of life. There are trillions of cells in the human body. Different cells have specialized jobs to do. For example, our brain cells perform entirely more different functions than our heart cells. They do one particular job.
Tissue
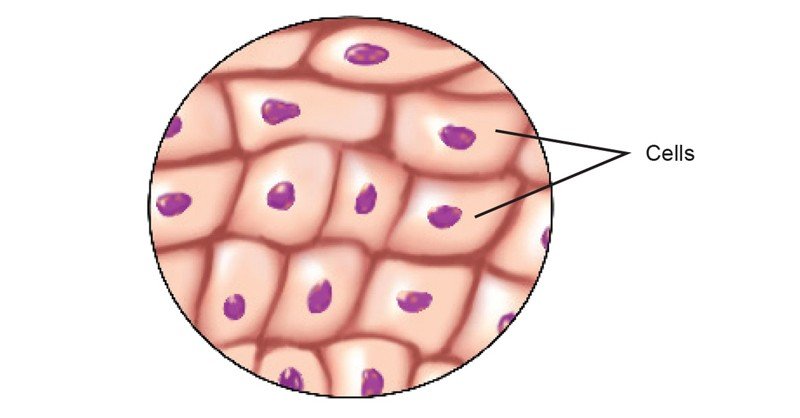
A tissue is a group of similarly structured cells woven together that perform a specific type of function in an organ. All cells of tissues have common origin. For example, nervous tissue has nerve cells or neurons, which are the same structurally and functionally.
Organ
The different types of tissues join together to perform a specific function. This association of tissues is known as an organ. For example, a human heart is made up of muscle tissues, nerve tissues, blood tissues and connective tissues.
Organ System
An organ system is a group of various organs that work together to perform a specific function. For example, a muscular system helps in the movement of the body.
| Organ system | Function |
| Skeletal system | Support and protection |
| Muscular system | Movement and locomotion |
| Respiratory system | Breathing/exchange of gases |
| Circulatory system | Transport of blood |
| Excretory system | Waste removal |
| Digestive system | Digestion and food absorption |
| Endocrine system | Regulation |
| Reproductive system | Reproduction |
| Nervous system | Control and coordination |

