Although it is almost impossible to translate the great life of Edison in words because his real character ever lived inside the creative and inventive centre of his mind, too busy to show itself to the mundane world. A person’s life is not a catalogue of his physical acts, gains and losses. The larger part a character means its thoughts, sentimental values and emotional waves or undercurrents.
The famous characters are more prone to these aspects because they generate or evoke professional rivalry, jealousy, envy, exploitative elements, enmity, emotional hurt, intrusion into privacy, strong reactions or protests capable of distorting the real image and the bitter fights to occupy his emotional spaces. But for the purpose of drawing up the broad picture of a famous character the events of his life do help and in them are vaguely reflected the sentimental and emotional patterns an intelligent reader can see through in varying degrees of clarity and correctness.
But the events of life of a celebrity can be inspirational as they show how a person of humble background or weighed down with handicaps can override the disadvantages and earn greatness through hardwork and ingenuity. The life of Thomas Alva Edison in periods can be classified in the following manner :
The life
11-02-1847 Born in Milan, Ohio
1847-1854 Time spent in Milan
1854-1863 Entered into teens in Port Heuren, Michigan
Hawked newspapers and toffees in Grand Trunk Railroad trains and station.
Published The Weekly Herald.
The station agent of Mount Clemence Michigan introduced Edison to telegraphy.
Worked as telegraph operator in Books & Jwellery store, Port Heuren owned by M. Walker.
1863-64 : Returned briefly to Port Heuren.
Served as night shift railroad telegrapher in Adrian, near Michigan and met Ezra Gilliland for the first time.
Worked as railroad telegrapher for two months in Fort Wayne.
1864-65 : Gained experience as telegraph repeater in the company run by Western Union office.
Served in Western Union Co., Cincinnati, Ohio and handled ‘self-adjusting relays’.
Become founder member of National telegraphic Union of Cicinnati in September.
Promoted as First Class Telegraph Conductor in the some month.
Developed a device for multi-dimensional telegraphy.
1865-66 : Worked as Press Wire Operator in South-Western Telegraphic Company Office.
Experimented in repeater related matters.
1866
June 4 : Appointed as Press Wire Operator in Western Union office of Louisville.
August 1 : Travelled from New Orleans, Los Angeles to Brazil for establishment work.
1866-67 : Returned to Western Union, Louisville.
June : Joined Cincinnati office of Western Union.
October : Came back to Port Heuren.
1868
March-April : Worked as operator in Western Union head office of Boston.
April 11 : Telegrapher magazine printed articels written by Edison on telegraphy, researches related to it and Boston telegraph community details.
July 11 : Signed contracts with E. Baker Wych in basic form. He was a Boston businessman who had financed Edison’s primary researches.
July 28 : Signed document turning over research on ‘Danger Alarm’ device to E. Baker.
October 13 : Applied for patent rights of ‘Electric Vote Recorder’ and later it become his first officially recognised and recorded patent.
1869
January 21 : Sold rights of successful Printing Telegraph to Joel Hills and William Plummer, the industrialists who owned Boston Instrument.
January 30 : Resigned from the services of Western Union Co. for studying and surveying various telegraph enterprises or works to apply himself fully to telegraph researches.
March : Joined hands with Frank Hennaford who was engaged in telegraphic private line trade.
April 13 : Failed in the attempt to establish double transmitter system between Rochester, New York and New York City.
April-May : Shifted to New York.
June 22 : Gained first patent in telegraphy on Boston instrument developed by him.
August 1 : Took charge of the post held by Franklin Pope, the manager of ‘Gold & Stock Reporting Telegraph Company’ of Samuel Law for the purpose of upgrading Law’s stock printer.
September 12 : Shifted to Elizabeth, New Jersey and lived with the mother of Franklin Pope.
October 2 : Did the task of advertising for the partnership firm of Pope and James Ashley. The firm was for electrical engineers and telegraph contractors.
December : Set up workshop for electric instrument and implements in New Jersey.
1870
February 10 : Signed two contracts with George Ford and Elisha Andrews of ‘Gold & Stock Telegraph Company according to which finance was to be arranged to set up workshop and lab for research for inventions.
February 15 : Assisted in establishment of principal workshop ‘The Nework Telegraph Works’ of Mr. William Ungar.
April 17 : Signed contract related to printing telegraph patents with Pope and Ashley for Gold & Stock Telegraph Company’.
May : Contracted Lamuel Cerel as his spokesman on patents.
July 1 : Set up enterprise to work for ‘American Printing Telegraph Company through ‘Private Line Telegraphs’ in association with Pope, Ashley, Marshal Lefferts and Willaim Allen.
August 3 : Signed a contract with Herrington in respect of upgraded perforator for automatic telegraphy under which finance was arranged for Edison’s experiments on automatic telegra

October 1 : Gained partnership in American Telegraph Works’ with George Herrington through a contract which provided for finance to facilitate his experiments for upgrading automatic telegraph systems.
An agreement was worked out for the sale of Edison’s new Universal Private Line Printer to ‘Gold & Stock Co. in association with Marshal Lefferts.
October 26 : Charles Bachelor joined services of American Telegraph Company.
November 28 : The Automatic Telegraph Company became public limited organisation and George Herrington was nominated its president.
December 1 : The company set up by Pope and Edison was closed down through a declaration.
1871
April 4 : Edison gave power of attorney to Mister Herrington to enable him to manage the shares of all automatic telegraphy inventions made by him.
April 9 : Nancy, the mother of Edison died.
April-May : Left Railroad Avenue to join the ‘Newark Telegraph Works’. The name of the firm was changed to ‘Edison & Ungar Company’.
Cotton Instrument was developed for Gold & Stock Company under a contract signed with Fiel & Andrews.
May 21 : The rights of the existing and future inventions were sold to Gold & Stock Co. in respect of the printing telegraph patents and Edison was appointed as Electrician Advisor of the firm.
July 28-29 : Four series of note books were started to register all the details of the inventions related to automatic printing and the telegraphy.
August : Developed ‘Stock Printer’ for Gold & Stock Company.
November 22 : Purchased first residential house in Right Street of Newark.
December 25 : Married Mary Stilwell, worker in his own office.
1872
January 27 : Converted ‘Universal Private Line Printer’ into ‘Electric typewriter’ of automatic telegraphy.
January-February : Registered the variations of Universal stock printer and Universal private line printer in the notebook.
February 5 : Became partner in J.T. Murray & Company. The firm later became ‘Edison & Murray Company.’
May : Provided ‘Gold & Stock’ company upgraded Universal line printer.
May-June : Supplied Universal stock printer to Exchange Telegraph Company of London.
July 3 : Edison bought all the shares of Edison & Ungar Co. and the partnership was dissolved.
November 5 : Signed a contract with Jozia Reef according to which Edison was to get an annual salary to further upgrade automatic telegraph.
December 14 : Edison upgraded the automatic telegraph and ‘Automatic Telegraph Company’ started marketing it.
December : Automatic telegraph system was tested at two places, Washington and Charleston for the benefit of Automatic Telegraph Co. and Atlantic Telegraph Company.
1873
February 10 : After a meeting with William Orton, the president of Western Union on oral agreement was reached for research on Duplex Telegraphy.
February 18 : The first daughter of Edison Marian Estele was born at Newark.
March 31 : Gained approval to manufacture Roman letter automatic telegraph for ‘Herrington and Reef’.
April 9-22 : Ten Patent proposals were prepared in respect of Duplex Telegraphy.
April 23 : Sailed for England.
May 23-27 : Gave demonstrations of automatic telegraphy system to British Post Office.
June 9-15 : Gave experimental and practical demonstrations of automatic telegraph in the Greenwich Laboratory for Telegraph Construction and Maintenance Company.
June 25 : Returned to Newark.
August 2 : Draft of ‘Caveat’ in respect of Quadruplex Telegraph was prepared.
August 25 : Application for patent right on Roman letter automatic telegraph perforator was submitted.
September 2 : Automatic telegraph rights were sold to a company for business in England.
September 6 : Did successful experiments using carbon current resistant rheostat in artificial cable telegraph.
September : Studied books on chemistry and experimented with amalgamation of various metals and chemicals for use in automatic telegraphy and telegraph recording paper. In this respect Edison applied for four patents. Began research in Three pin automatic telegraph perforators.
October 1 : Demonstrated Quadruplex telegraph for important telegraph offices.
October 28 : Registered Caveat in respect of automatic telegraph circuit regarding Roman letters.
November : Appointed Charles Bachelor his principal laboratory assistant and started experiments on electro-chemical solutions in batteries.
November : Worked with Jessie Benale, the inventor of telegraph and a manufacturer on a railway signal instrument.
December : Did successful experimentation in automatic telegraph system for important telegraph authorities.
1874
January 27 : The Automatic Telegraph Co. gave a public demonstration of Edison made Automatic telegraph system.
February 1 : The draft on ‘Caveat and bar’ in respect of the new Roman letter automatic telegraph was finalised.

February : Extensive experiments were carried out to solve problems of cable telegraphy related automatic telegraph recordings. The investors and industrialists of England requested Edison to personally supervise the experiments being carried out related to automatic telegraph operated by British Post Office and private cable lines.
February : Prepared to work on the proposed book on telegraphy.
March : District telegraph and fire alarm system research work was carried forward.
March 26 : Joseph Murray and Jarvis Adison was joined in by Edison to set up a joint firm called ‘Domestic Telegraph Company’. It was proposed that the firm would market the invented products of district telegraph and fire alarm systems.
March : The president of the Western Union, William Orton sanctioned financial assitance for research on Duplex telegraphy.
April 10 : The pioneering research on Electromotograph.
April 16 : Demonstrated Roman letter automatic telegraph system before George Ward, the American manager of ‘French & Anglo-American Cable Lines Company.’
April 18 : Experimented ‘Induction Coils’ for a electro-magnetic medical equipment.
April 28 : Set up a workshop with models to inspire student telegraph operators sponsored by a proposed scientific toy company.

May 19 : Reached at an agreement with Western Union electrician George Prescott for cooperation in Duplex project. According to the agreement they were to be 50-50 partners in inventions resulting from experiments carried out through it.
May 22 : Inductorios was marketed.
May : A research was undertaken on a metal called ‘Tellurium’ having similar properties as sulphur to benefit domestic telegraphy through usefulness of the recording system.
June 1 : An application was submitted to get the patent on ‘Tellerium recording stilus’ for the automatic telegraphy.
The proposal of Thomas Alva Edison was supported by George Prescott and William Orton by which the research on Quadruplex was to be done in Western Union Lines and the instruments were to be tooled in the Western Union workshop. It was approved.
June 21 : Contract of partnership with George Prescott about Quadruplex and Duplex signed.
George Harrington and Jozia Reef meet to talk about setting up of a new firm to commercially handle the products spun off by inventions in the field of automatic telegraphy made by Edison.
July 3 : Automatic Telegraph company paid money to Edison raised from the investors on the basis of the pledge signed by him. It became possible due to the efforts of Herrington and William Ungar.
July 8 : Quadruplex telegraphy system demonstrated before officials of Western Union Company at the company lines.
July 9 : First partnership contract with George Prescott signed.
July 10 : Western Union Co. introduces and defines Quadruplex in an article in New York Times.
July 18 : James Ashley a former partner of Edison got an item published in Telegrapher using objectionable and scurrilous language against Edison.
July 24 : Accomplished some automatic telegraph models for George Herrington and upgraded the British Wheatstone system to modernise.
August 3 : Again started using Electromotograph.
August 7 : Applied for patenting the telegraph device in which electromotograph was used.
August 19 : Signed redrafted partnership contract with George Prescott and forwarded applications for the patents in respect of Quadruplex and Duplex.

August : Became Editor of a science journal called Operator. James Adams became lab associate of Edison.
September 1 : Operator printed some articles of Thomas Alva Edison, as his pioneer writings.
September 5 : Scientific America published the announcement of the invention of Electromotograph.
September 21 : Received tips and training in some aspects of chemistry from Robert Spice the professor of chemistry and natural elements of Brooklyn High School.
September : Successfully demonstrated Quadruplex at Western Union line between New York and Boston. It was agreed to start commercial activities from October 3.
October : Use of Quadruplex on Western Union lines began and it was also upgraded.
November 1 : Shifted to Bank Street house with his family.
November 2 : Started experiments in search of new sources of energy.
November 6 : Demons- trated Electromotograph in the of the Science Academy of Philadelphia.
December 1 : Sold his Right Street house.
December 3 : Agreement reached to establish Domestic Telegraph Company in Canada and started work on new private line printer for the Domestic system.
December 4 : Caveat was issued in respect of first four of the twelve multi-dimensional telegraphy and application drafted for the patent rights of the same.
Quardruplex system successfully demonstrated through Western lines between New York and Chicago.
December 9 : The names of Edison and Charles Bachelor included in the Engineers Society of London.
December 10 : Received $ 5000 as advance from Western Union for Quadruplex systems.
Mid-December : Negotiated with Western Union for the sale of Quadruplex system. President Orton of W.U. undertook business trip.
December 30 : Contract to take over Atlantic and Pacific Telegraph Company signed by Jozia Reef, Mackmanes and J. Gould. Edison appointed as Electrician of the company.
December 31 : Because of possible or anticipated hurdles Quadruplex patent application was deferred.
1875
q January 4 : Quadruplex patent rights sold to J. Gould for $ 30,000 only.
q January 5-8 : Held meeting with J. Gould to discuss strategy to deal with the situation arising out of rivalry between Western Union and Atantic & Pacific Company.
January 14 : Returned to family at Port Heuren, Michigan.
January 19 : William Orton agreed to the terms set by Edison for the sale of Quadruplex.
January 20-21 : Revised and logical application was submitted about the applications for patent rights for all multi-dimensional telegraphic inventions made upto December 31, 1874 for immediate registration as patents where there was no adjournment.
January 23 : The Commissioner of Patent Office was informed that Quadruplex patent was to be registered jointly with Herrington and Prescott was to be left out of it.
January 28 : Western Union began legal proceedings against Edison in New Jersey in respect of the rights of Quadruplex.
January : Edison inspected New York-Boston line of Atlantic & Pacific Co. as electrician.
Edison and Murray started the production of Domestic-telegraph device for New York
city lines. And for Atlantic & Pacific Co. automatic instruments were also produced.
February 11 : On the birthday of his wife Mary Edison a fancy dress party was organised where the guests came in various disguises.

February 24 : Submitted application for the patent rights of Domestic telegraph system jointly with Charles Bachelor.
February 27 : J. Gould agreed to bear all the expenses on the experiments to upgrade the automatic system of Roman letter telegraphy.
March 20 : The Patents Secretary passed an order on Qudruplex system saying the patent would be in the joint names of Edison and Prescott instead of Edison and Herrington.
March 23 : Two patent applications were submitted in respect of Quardruplex repeater and Domestic telegraph system designed jointly in association with Charles Bachelor.
March : Demonstrated automatic telegraph system based on spectroscope before Secretary of German Telegraph Systems.
March-April : Went to South Orange, Newark residence with family.
April 1 : Ezra Gillitand’s new store of Newark started selling Edison-Murray products.
April 16 : After agreement with Atlantic & Pacific Co. the interests of some patent rights of automatic telegraph system were decided to be shared with George Herrington and Jozia Reef.
April 20 : Gold & Stock Telegraph company agreed to settle the overdue accounts.
To assess the financial status of Edison his properties and liabilities were balanced.
April 27 : Application for reconsideration along with a pledge submitted by Edison against the earlier Quadruplex order of Patents Commissioner was forwarded to the Secretary of Internal Appeals.
April 30 : Research and experiments to upgrade the copying process was undertaken.
May 7 : Experiments on Electromotograph began for the automatic telegraphy.
May 16 : Production partnership with Joseph Murray was terminated and Edison set up a lab separately at Ward Street workshop.
May 31 : A list of proposed subjects for research in association with Charles Bachelor was prepared and experiments started in the new laboratory.
June 2 : New energy source needed for research in telegraphy was underlined.
June 30 : Faximile system for electric pen was revealed.
July 15 : Formalities for the end of partnership with Murray was duly completed.
July 26 : Lease deed to conduct night paper business of Atlantic & Pacific Wires Co. from the laboratory was proposed.
July : Discussed acoustic telegraphy with William Orton in a meeting.
Plant and machinery works for setting up of manufacturing unit by Ezra Gilliland & Co. at Ward Streetwork shop was accomplished.
August 5 : The final list of inventions upto 1876 meant for 1876 Millenium Exhibition to be held at Philadelphia was prepared.
August : Some suggestions were made to solve the disputes regarding automatic and Quadruplex system for patent related agreement. It also would set the terms for settlement between the Atlantic & Pacific Co. and Western Union.
September 16 : Proposal made for Duplexing the Atlantic cable from United States Cable Co.
Mid September : Invented original Electric Pen Copying System and manufacture-marketing of the same was started.
September 23 : First warning against duplicacy of electric pen copying system issued. Went to Port Heuren to be with the family.
October 1 : Contracted some agencies in respect of electric pen including his nephew Charles Edison.
October 2 : Agreed to give some percentage shares in the profit from the sale of electric pen to Charles Bachelor and James Adams.
October 5 : Presented a system to transmit the messages of share brokers to New York Stock Exchange.
October 14-21 : Invented new battery for the electric pen.
October 31 : Taking inspiration from other inventions prepared warning against duplicacy of Faximile telegraph taking cue from Electro-motograph and the electric pen.
November 16 : Edited experiments related to acoustic telegraphy experiments in Western Union.
November 22 : Issued warning in respect of acoustic telegraphy and presented Quadruplex in a new form. While working on accoustic telegraph devices an Etheric Force was held responsible for some interferences. Researched on this new force.
November 29 : Gave interview to correspondents of press about that Etheric Force.
Gave assent to sale of automatic telegraphic rights to New American Automatic Telegraph Co. under a strategy to harmonise the interests of Atlantic & Pacific Co. and J. Gould with American Automatic.
December 14 : Realised the need to settle counter claims born out of controversies over Quadruplex rights with Western Union whose cooperation would be useful in the research of acoustic telegraphy. It could gain Edison full control over the rights of his inventions.
Experimented on Etheric Force in the Stevens Institute of Technology, New Jersey in association with Professor Henry Martin.
December 16 : Gave demonstration of Etheric Force in a seminar at American Institute, New York organised by Polytechnique Association in the presence of Dr. George Beard.
December 23 : Gave demonstration of Etheric Force in the meeting of Newark Scientific Association.
December 29 : Bought land in Menlo Park for new house and laboratory.
December : All through the month experimented on acoustic telegraphy.
1876
January 10 : First son Thomas Alva Junior was born at Newark.
Mid January : Revised Caveats were settled in relation to acoustic telegraphy.
January-February : Did his acoustic telegraphy experiments in his lab and on Western Union lines at practical level.
Demonstrated new Quadruplex on Western Union lines. Construction of lab, workshop and house on his Menlo Park land began under the supervision of his father.

February 7 : Made electric pen more useful. Changed laboratory instrumentation and began manufacture in Gilliland & Co. facility.
February 8 : Signed contract with the father of Ezra Gilliland that gave 10% share in the electric pen to Gilliland.
March 7 : Prepared draft of the application for patent rights of Electric Pen Copying System. It was submitted on 13th March. It was the first application of Edison in a year.
March 7 : Public issue of New Electric Pen Company came out.
March 13 : Agreed to take part in Millenium Exhibition with Western Union.
March 16 : Mary Stilwell organised a surprise party at the Edison house.
March 21 : Applications for the patents of Qudruplex and Automatic Telegraph were withdrawn and objection was raised based on the power of attorney given to the lawyer. It was in reaction to the earlier adverse order of the Patents Commissioner. There was argument with people over the nature of the Etheric Force.
March 27 : Arranged for agencies abroad for electric pen in association with Charles Bachelor.
March 26-28 : Shifted the family and lab to his new Menlo Park facilities.

April 3 : After settling down at Menlo Park first appreciation for patent of Acoustic Telegraphy was submitted.
April 4 : Atlantic & Pacific Telegraph Co. filed a suit against Edison, Lamuel Cerel, Western Union and George Prescott in respect of patent rights of Quadruplex telegraph system.
April 5 : Sold his stock in Domestic Telegraph Company.
May 1 : Marshal Lefferts was contracted for working out foreign rights of electric pen.
Concentrated on the research of Acoustic Transfer Multiple Telegraphy and started experiments in the new laboratory.
May 10 : In Millenium Exhibition of Philadelphia the inventions of Edison were displayed as stellar exhibits of the show.
May 11 : A suit was filed against Western Union, George Prescott, interim secretary J. Chandler and Patent Commissioner Rudolph Dual by Edison, Herrington and Jozia Reef in Washington to prevent Edison’s Quadruplex patent being awarded to Prescott and Western Union jointly.
May 13 : Filed another suit with Herrington and Jozia Reef against Atlantic & Pacific T. Company and J. Gould in New York to get the payment for Edison’s automatic telegraphic inventives from them.
May 26 : Renewed the five year contract with Gold & Stock Co. regarding patent rights and salary.
May 31 : Issued extensive objection notice for his Acoustic Telegraph System.
June 7 : Realised the danger to his acoustic telegraph invention from Elisha Gray and A. Graham Bell’s questioning his patent rights.
June 25 : Graham Bell exhibited his telephone in the Millenium Exhibition.
Thomas Alva Edison received awards for his achievements in Automatic Telegraph System, Electric Pen and Autographic Press.
July 3 : Marshal Lefferts died. He was a guide and friend of Edison and served as the president of Gold & Stock Company.
July 10 : Sold British rights of electric pen to John Bracken and Thomas Clair.
July 18 : British scientist and engineer William Thomson paid a visit to Menlo Park works of Edison.
July 24 : In reaction to critical comments of E. Thomson and A. Houston on Etheric Force Edison stopped experimenting on it.
July 25 : Experimented acoustic transfer telegraph systems on Philadelphia line.
July : Several experiments were carried out in the series of telephonic subjects.
August 3 : Experimented on Electromotograh for two months and made its use possible in automatic telegraph repeater and galvanometer.
August 15 : John Bracken and Thomas Clair set up Electric Writing Company in Great Britain for the distribution of electric pen.
August 28 : Proposal for share stock received by Edison in Port Heuren & G. Railway Company.
August : Recorded statement for patent related intervention after dispute over Acoustic Multiple Telegraph Designs arose with Elisha Gray.
September 7 : Gained information in respect of Morse Telegraph Recorder/Repeater.
September 13 : Tested Octruplex Acoustic Transfer system on Philadelphia lines.
September : Experimented on Carbonised paper to make it electric resistant and make it effective in battery carbons too. It also was for use in crucibles and other utilities.
October 18 : Experimented with electro-magnet to add speed to saving machine using tuning fork.
October 30 : Submitted two patent applications. One was about adding speed to sewing machine with tuning fork and the other was regarding perforator of Telegraph recorder/repeater.
November 3 : Edison discovered that the chemicals used in lab got destroyed by sun light to a major extent. He experimented on chemicals and studied the effects deeply. His article detailing his funding was published in American Chemicals.
November 28 : Agreed to aquire with Western Electric Company and turned it into manufacturer of electric pen and press copying system and domestic sales agent of those products.
December 1 : Invented Duplicating Ink for multiple copying of documents and it was marketed in U.S.A.
December 10 : Stormy wind damaged the lab building of Edison and Chemical stock also were affected due to below zero temperature.

1877
January 6 : Restudied the two cases of intervention in respect of two patents related to Acoustic Multiple Telegraphy institute and were benefiting Elisha Gray at various levels formally.
January 8 : Drafted proposal for small electric motors for distribution of American Novelty.
Mid January : Carried on deep experimentations in a series on chemicals and etheric force.
January 17 : Prepared a map of a plan with Charles Bachelor and proposed to George Bliss to set up a Foreign Electric Pen company.
January 18 : The former landlords of Edison, Ezra and R. Gould of American Telegraph works Newark filed a suit against him.
January 19 : Agreed to give distribution rights of Duplicating Ink, Door Indicator (of Bachelor) and Johnson’s Ribbon to American Novelty. Bachelor and Johnson were in Edison’s team.
January 20 : Carried out elementary experiments on telephone transmitter and electric resistance was differentiated by manipulating the carbon pressure instead of quantity.
January 29 : A new agreement draft was draw with Western Union to gain cooperation of the company for his laboratory.
February 2 : Objected to J. Gould for his dealings with Atlantic & Pacific Co. and Thomas Accurt.
After receiving proposal from Edison Port Heviren Street Railway agreed to boost the stock holdings.
February 3 : Application for a patent for the crafted recorder/repeater was submitted.
February 8 : Primary experiments on double plate crafted recorder/repeater were started.
February 9 : George Prescott, the electrician of Western Union Co. visited Menlo Park laboratory for experimentations on recorder/repeater and telephone.
February 15 : Edward Johnson suggested the name of American Novelty Co. be changed to Electro Chemical Manufacturing Company.
Mid February : The postponed research on the telephone were restarted.
February 19 : J. Gould was urged to settle the disputes regarding the rights of Quadruplex inventions with Western Union.
February 26 : Anson Stegger and George Bliss visited Menlo Park facilities to discuss the foreign rights over electric pen.
February 28 : Set out for Port Heuren to take part in seminar organised by Port Heuren and G. Street Railway Company.
Charles Bachelor accompanied Edison upto Port Heuren and moved on to Chicago to work out settlement of Electric Pen accounts with Western Electric Company.
March 12 : Returned to Menlo Park.
March 14 : Demonstrated the double plate crafted recorder/repeater at the head office of Western Union, New York.
March 18 : Invented first Electromotograph Telephone receiver.
March 19 : Demonstrated his telephone device on Mento Park live for officials of Western Union.
March 21 : His father Samuel visited Menlo Park.
March 22 : A contract was signed with Western Union according to which the company agreed to give financial assistance to Menlo Park lab of Edison and in return the company was to have some percentage share in Edison’s all future telegraph and telephone patents.
March 23 : Application for patent rights prepared for Saxtuplex Telegraph System and telephone.
March 30 : Joseph Murray got manufacture order of double plate six crafted recorders/repeaters from William Orton.
April 1 : Incentive design of telephone device became main basis and later invention of Microphone was claimed.
April 10 : Experimented on telephone transmitters designed basically on carbon.
April 18 : Applied for patent related to the telephone for the first time.
April 24 : Signed a contract with Bachelor, George Bliss and Charles Holland for distribution of electric pen in Europe.
April 26 : In Quardruplex case of New York worked on proof-witness matters against Atlantic & Pacific Co, Prescott and others.
April 28 : Gave demonstration of musical Electromotograph Telephone for seven days in Newark Opera House.
May 3 : First hearing of Quadruplex case took place.

May 16 : Signed a contract with his nephew Charles Edison and ex-agent of electric pen, George Cadwell according to which they could distribute Musical Telephone for demonstrations.
May 18 : British telegraph engineer, William Greece visited Menlo Park lab facilities.
Experimented for a month to explore the possibility of making telephone transmitter based on pencil lead, Plumbago. Under a contract George Prescott and Gerrit Smith agreed to form a union for British quadruplex patent.
June 4 : Electromotograph Manufacturing Co. transferred the rights of duplicating ink and ribbon muchilage to George Bliss and George Holland and one month later they aquired foreign rights as well.
June 5 : Succeeded in designing Combination telephone transmitter and electromotograph receiver.
June 8 : Sextuplex was tested on Western Union line between New York and Boston. But later after a lot of considerations this idea was dropped.

June 28 : Final hearing in Quadruplex case took place pending the verdict.
July 2 : Samuel deperted from Menlo Park for Port Heuren residence.
July 3 : Mouled recorder/repeater was demonstrated before Western Union authorities, British Telegraph officials, William Greece and Hanry Fischer.
July 17 : Visualised telephone message recorder/receiver.
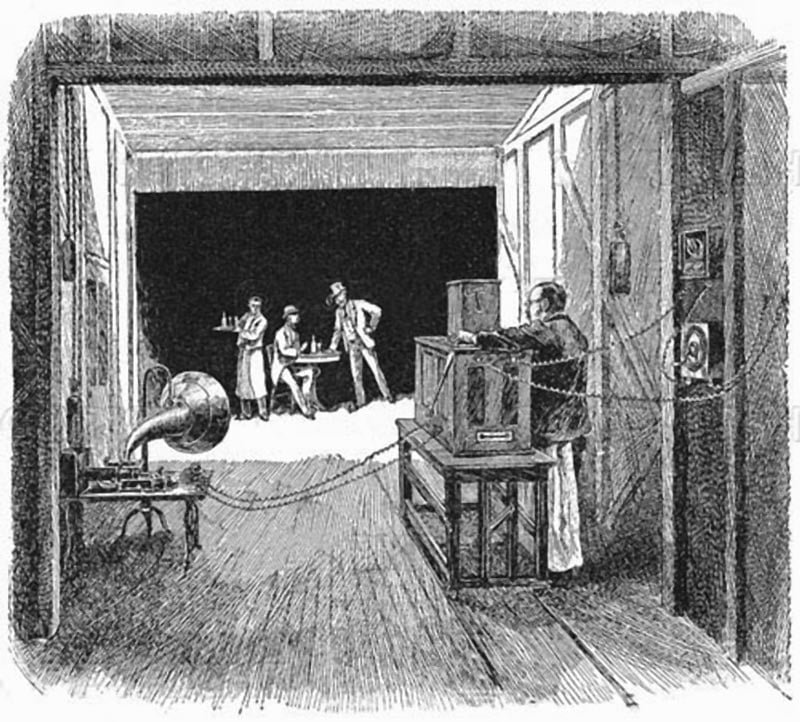
July 18 : Visualised Phonograph.
July 19 : Edward Johnson and George Barker gave demonstration of Edison’s musical telephone in Phidadelphia Exhibition Hall before a huge crowd of admiring people.
Formalities for British telephone patent completed and details about phonograph also attached.
July 21 : Scientist George Barker, Henry Dropper and a manufacturer, William Wallace visited Menlo Park facilities.
July 27 : Alex and Siemans, the nephew of William Siemans saw Menlo Park laboratory.
July 30 : Carbon fibre was used for telephone transmission.
August 1 : In the second demonstration of musical telephone at Philadelphia Edward Johnson gave a speech as well. The exercise continued for a year.
August 3 : Corresponded for one month with Henry Dropper to exchange views and ideas on
.August 4-10 : Carried experiments in Menlo Park lab with Thomas David related to telephone.
August 7 : Sent Charles Edison to Port Heuren to represent his interests in Street Railway.
August 10 : Joseph Murray gave demonstration of combined transmitter-electromotograph (self made) befor Western Union officials and tested on New York city line.
Mid August : Tested various telephones on New York city lines.
August 20 : New design telephone was demonstrated before William Orton, the president of Western Union and other authorities.
August 21 : Western Union signed contract to buy controlling powers of Atlantic & Pacific Co. and in this way the rivalry and legal entanglements of the two corporations ended.
August 24 : Visualised hand held telephone and the design was worked out.
August 25 : Robert Watson of Montreal visited Menlo Park lab to get Edison’s telephone to Canada.
September 9 : Resigned as Electrician of Atlantic & Pacific Co. Experiments started on electric arc lights.
September 10 : Began experiments on thermal power produced electric lights.
September 15 : Signed contract with Franklin Baudgar, the associate of Robert Watson in respect of distribution of telephone devices in Canada.
September 17 : Demonstrated a new transmitter before William Orton. Orton placed an order of 150 sets of transmitters/receivers for Gold & Stock Co., a subsidiary of Western Union.
September 18 : Proposed to George Bliss that he and Charles Holland buy European patent right of Edison telephone.
A joint contract was signed by George Prescott, Stephen Field and Ornelouis Hertz in respect of European patent rights of Quadruplex system.
September 28 : Successful experiments of Quadruplex 4telegraph carried out by Gerrit Smith and George Hamilton on British Post Office lines.
September 29 : The first patent applicant of the telephone was shifted under new patent laws. The Patent Office wanted to end the disputes and controversies over patents through amended laws.
October 5-8 : Joseph Murray produced telephone transmitter was redesigned in new form.
Won the legal battle over Henry Truman in respect of electric pen patent dispute.
October 18 : Took part in telephone exhibition organised by Edward Johnson in Jersey city.
October 22 : Experimented with lamp black and rubber in telephone transmitter.
November 17 : Western Union set up American Speaking Telephone Company. The company used Edison’s telephone patents and patents of Elisha Gray, the owner of Harmonic Telegraph Company.
Mid November : Invented use of magnetised coil circuit in telephone.
November : Proposed carbonless alternate transmitter design.
December 1-3 : Experimented with the use of magnetised coil circuit in telephone.
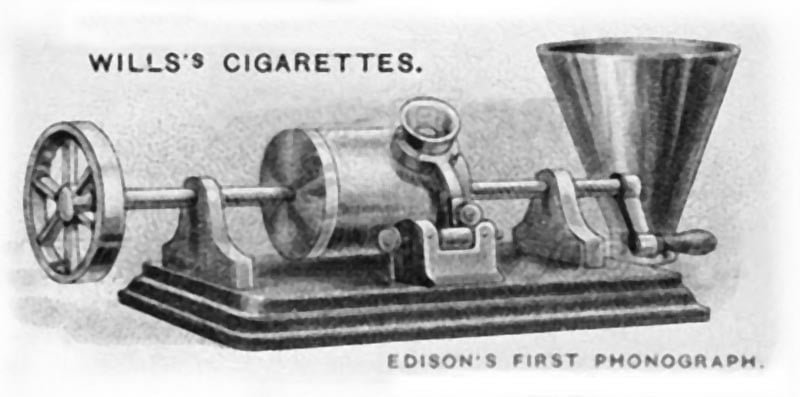
December 1-6 : John Crusoe made first tin-foil cylinder phonograph.
December 7 : The cylinder phonograph exhibited and demonstrated in Scientific American office of New York.
December 12 : Edison won the dispute against Edward Steward regarding electric pen patent.
December 15 : First application submitted for the patent of phonograph.
December 17 : To earn profits from patent lights of European telephone and phonograph a contract was signed by George Bliss with Hungarian Count Theodor Puscess.
December 26 : Carried out experiments on phonograph recording on telephone in New Jersey.
December 27 : Held a meeting in Menlo Park with Edward, Johnson and Gardner Hubbard to discuss disassociation from Western Union and setting up a new company to market phonograph.
December 29 : Edison was nominated as a Scientific member of American Commission to represent in Universal Exhibition 1879 Paris.
December 31 : Demonstrated phonograph in front of William Orton.
1878
January 1-3 : Gave demonstration of phonograph in Western Union office of New York.
January 3 : Designed Fly wheel Phonograph.
January 7 : Contracted manufacturers for making phonographic toys and clocks.
January 8-10 : Tested telephones in the offices of Western Union. Felt uncomfortable with electricians of the company.
January 12 : William Orton was made trustee of British Quadruplex patent rights by George Prescott and Gerrit Smith.
January 23 : Theodor Puscess goes to Europe as agent of Edison’s phonograph and telephone inventions.
January 29-30 : Visited Ensonia Clock Co. with Charles Bachelor and experimented with phonographic clocks.
January 30 : Signed a contract to reap commercial benefits from phonograph in USA.
January 31 : Through flywheel phonograph pictured a scientist and an technical figure.
British investors laid claims on Quadruplex strongly and readied for a legal battle.
Edward Johnson took upon himself the responsibility of addressing publicly the need of upgradation of Edison’s phonograph and carbon telephone.
February 1 : William Greece and John T. gave a demonstration of phonograph in Royal Institute of London. It was the first demo of the device outside USA.
February 6 : Small phonograph was designed and exhibited in Universal Exhibition of Paris. It was for sale as well.
February 10 : Tested carbon telephone transmitter on lines between New York and Philadelphia in association with Henry Bentley.
February 19 : The first patent on phonograph gained.
February 22 : It was decided to produce telephone receiver that would not violate the patent rights of Grahm Bell.
February 28 : Extensive caveats were issued in respect of phonograph and telegraph and three patents were applied for. These were for Telephone Station, Call Signal device and technique to deal with telephone line disturbances and Aerophone.
March 1 : James Adams was sent to Philadelphia to assist Henry Bentlay in telephone testing and demonstrations.
March 2-8 : Edward Johnson became Principal agent of prospective phonograph company and he ordered the production of phonographs of commercial use.
March 15 : Negotiated for a contract with William Orton, the president of Western Union about a new telephone.
March 19 : James Adams was sent to London to test telephone transmitters on British Post Office lines.
March 20 : Gave public demonstration of a upgraded carbon telephone transmitter in Franklin Institute, Philadelphia.
March 20-21 : Experimented on hand operated phonograph and attempt was made to develop a disc phonograph.
The strength of workers in Menlo Park lab increased.
March 22 : Discussed the matter of commercial operation of phonograph in Great Britain with Count Theodor, then contract was signed with ‘London Sterioscopic & Photographic Company’.
March 26 : A notice was issued regarding the telephone patent embroglios, delays and long drawn disputes or rivalries.
March 29 : New York World published Edison’s cures for ailments and medicinal formulae.
March : The press gave wide coverage to the deeds of Thomas Alva Edison who was now an iconic figure. People flocked top Menlo Park to pay their tributes.
Consulted Gardiner Hubbard about aquiring the rights of Bell Telephone Co. under his own carbon transmitter venture.
April 6 : Loaned money to Joseph Murray to enable him to pay the rent of Ward Street shop in Newark.
April 8 : George Bliss wrote biography of Edison in ‘Chicago Tribune’.
April 10 : New York Daily Graphic gave Edison the epithet of ‘The Magician of Menlo Park’.
April 18-19 : Demonstrated phonograph before the members of Congress and National Academy of Sciences.

April 19 : Washington Star printed the introduction of Edison’s invention ‘Tasimeter’, its basic principles and some elementary information. It also gave brief account of Edison’s device that enhanced hearing power of a person.q April 22 : William Orton, the president of Western Union passed away.
April 24 : Edison’s speaking Phonograph Company became incorporated.
April : Edward Johnson wrote ‘The future of phonograph anonymously for ‘North American Review’.
May 1 : A world level exhibition of the inventions of Thom Alva Edison was held in Paris.
May 6 : Viewed the infection of marcury through a borrowetelescope.
May 8 : Urged Charles Harris to contract John Autt to manutoy phonograph at Menlo Park

May 18 : Prepared new design of Tasimeter.
May 29 : Issued Caveat in respect of European patent of phonograph.
May 30 : Gave a demonstration of phonograph with his assistant at ‘The Convent of Mount 86. Vincent’ a Catholic girls school of New York.
May 31 : A contract for $ 6000 a year for 17 years was signed with Western Union in respect of telephone patent rights.
Edison Speaking Phonograph Co. contracted James Redpath for conducting phonograph exhibitions.
Some sale agencies were set up in central and South America and Australia for sales and distribution of phonograph and telephone.
June 1 : George Garout was appointed agent for Great Britain.
Stockton Griffin became Secretary of Edison.
June 2 : Charles Edison began experiments to invent a kind of telephone receiver that had no previous patent.
June 12 : Sales agreement was signed with Patrick & Carter of Philadelphia for 25 telephone transmitting sets.
June 26 : Union College of New York conferred Honorary degree of Doctorate on Thomas Alva Edison.
June 30 : Started research work on Hearing aid and other hearing devices.
July 13 : Went to Rollins with George Barker to view the sun eclipse and stayed on a month long holiday in Western United States.
July 17 : Provided financial assistance to Patrick Kenny for faximile industries.
August 1 : Some upgradation work was done on phonograph demonstrations by Charles Bachelor and Edward Johnson.
August 9 : Spent night in Virginia city and inspected mines to study heat and air flow problems in the tunnels.
August 21 : George Bliss toured Chicago.
August 22 : A big award after the name of Edison was declared in Paris International Expo.
August 23 : Took part as a member in a seminar on ‘Science and Development’ organised by American Association in St. Louis. He presented his research paper on Tasimeter.
August 29 : Started experiments on electric light.
September 1 : Inspected electric light and energy devices at Ansonia workshop with Charles Bachelor, George Barker and Charles Chandler.
September 8 : Upgraded phonograph was displayed by Edward Johnson in New York city. Other invention of Edison were also exhibited.
September 10 : First caveat was issued in respect of electric light.
September 13-16 : Edison declared that problems related to electric light through heating process had been solved.
September 14 : Dynamo was received from William Wallace.
September 19 : Proposals from investors began to come in for the proposed electricity project.
September 21 : Count Theodor set up a company to gain benefits (commercial) of Edison and Elisha Gray telephones in France.
September : First patent application for electric light.
October 5-18 : Start of work on new phonograph according to the commercial considerations.
October 19 : Edison Electric Light Co. became incorporated. Basically its investors Western Union, Drexel and Morgan & Co. were related to it.
October 26 : In Menlo Park Edison’s second son William Leslie arrived.
October 30 : Investors got angered when William Sawyer and Alban jointly claimed that they were senior and superior in the field of electric light.
October 31 : Four caveats were registered in respect of electric light. A new steam engine, a Watson dynamo and a Wallace dynamo were purchased.
Construction of new machine shop and office building started.
November 6 : Negotiated with Lemual Cerel through Telegraph for patent rights of new lamp for Britain.
November 13 : The services of Francis Uptron were taken to deal with the panic gripping the share holders of Edison Electric Light Company by presenting technical aspects and scientific views or opinions of literature of accepted class.
November 15 : The light related patents of Edison Electric Co. were determined. Stock and royalty were approved along with $ 30,000.
November 20 : Two designs of dynamo were prepared and one was chosen for the British patent.
November 22 : Talks were held with Gold & Stock Co. about new electromotograph telephone receiver.
November 23 : After the support of Edison Edward Johnson and Urea Penter gained control of Edison’s speaking Phonograph Company.
November 29-30 : First electric meter was designed.
December 1-2 : To pacify the shareholders of Edison Electric Light Co. various electric light devices were demonstrated.
December 3 : First patent application submitted for Electric Generator keeping in view the concept of tuning fork engine.
December 14 : The lab workers began to shift equipments into the new building.
December 15 : Francis Uptron contracted to work as mathematical and lab assistant.
December : Charles Edison started his experiments on the new telephone receiver. G. Laurie, Drexel and Morgan & Co. negotiated with investors for foreign rights of electric light on behalf of Edisons. The construction of new dynamo after designing began.
1879
January 2 : The primary manufacture of the electric generator (Dynamo) gets due start.
January 19-29 : A series of experiments on the platinum and other metals carried on.
March 14 : Charles Edison tests his new electromotograph (high pitch) telephone receiver.
Rest of March : Designed bipolar generator device.
May 14 : European Edison Telephone Company is incorporated.
June 17 : Rhutgurs College, New Brunswick, New Jersey confers Honorary Doctorate in Philosphy on Edison.
Spring : Researched on extensive platinum mining in Canada, western and southern mine zones of USA.
August 2 : Played a role in organising Edison Telephone Company of London.
August : After contracting Glasblamer Ludwig started upgradation work of vacuum pump.
Improvised electromotograph telephone receiver for England.
October 14 : Signed contract with Jose D. Husband for sale of Edison telephones in Chile.
October 22 : First successful experiment with high capacity carbon resistance filament.
November 1 : Applied for patent of his resistance carbon filament. First application.
December 9 : Edison Ore Milling Co. proposed.
December 31 : First public demonstration of heating electric light at Menlo Park.
1880
February 13 : First study of Edison effect as to how it is known or detected.
Winter end : Increase in staff of Menlo Park. Worked for development of all aspects and factors related to heat electricity.
March 25 : Magnetism based ore separation system-experiments and tests carried out.
April : Electricity plant proposed in Columbia.
May 13 : Experiments on electrified railway carried out at Menlo Park facility.
July 3 : Grant provided for basic facilities for a science journal. Printing it became possible.
July 19 : First lamp with bamboo filaments experimented with and it later became standard for Edison lamps.
September : Manufactured direct connected dynamo by the name ‘Jumbo’ and it was used in Porter-Allen Steam Engine.
October 1 : Menlo Park situated Edison Lamp Works started commercial production of electric lamps.
December 17 : Played role in setting up Edison Electric Illuminating Company in New York.
December 20 : Electric lighting system was demonstrated at Menlo Park for New York city Elderman.
December 23 : Edison Electric Light Co. was incorporated in Europe.
1881
June 25 : Signed a contract with Alexander Graham Bell and others to establish Oriental Telephone Company.
February 28 : Appointed Samuel Insal his Private Secretary.
March 1 : Experiments Department was set up on Edison Lamp Works which became centre of lamp experiments.
March 10 : He began to run his business from 65, Fifth Avenue, New York city. Here Edison used to guide managers of his various electric light companies.
March : New York city became his home.
March-April : Found Edison Electric Lamp Company. Edison Machine works and his other companies manufactured lamps, generators, conductors and other instruments for electric light systems.
April 30 : Charles Huges was made incharge of experiments on fruit preservation through vacuum.
May 17-June 25 : 23 patent application submitted related to electric light.
June 26-30 : Installed horizontal conductors for Pearl Street Central Station of New York city.
July 1 : Charles Bachelor was sent to an international Electric Exhibition to oversee Edison show in it.
July 26 : Applied for Faximile telegraph patent in association with Patrick Kenny.
August 10 : In Paris Electric Exhibition Edison’s inventions were spotlighted.
September 14 : A contract was signed with Henry Billard according to which he undertook to give financial assistance to the projects of Edison.
September : Edison’s ore separator was used by his ore Milling Company in Rhode Island.
December : In Edison’s machine workshop a test wing was set up that became headquarter of electric lighting experiments and dynamo testing.
1882
January 12 : Edison’s Holborn central station began to work. It was situated in London.
January 17 : Crystal Palace London exhibited inventions made by Edison.
February-May : Companies were set up in London and Paris to manufacture electric light system devices and machines. They functioned as head offices for Europe and England enterprises. Electric companies were set up in Latin America as well.
May 8 : A series of researches and tests were carried out at Menlo Park lab related to electric lighting. Edison felt that the tasks undertaken by Edison machine works was more then it could handle.
In respect of electric lighting, electric railway and auxillary batteries applications for 53 patents were submitted.
September 4 : Pearl Street Central Station was set up in Wall Street, New York.
October 4- November 28 : 34 patents applications in respect of electric lighting and electric railway were forwarded.
November : Menlo Park laboratory was closed down and a new lab set up in Burgman & Co. factory of New York city.
1883
January 19 : Edison used electric lighting system through wires tied overhead in New Jersey. It was a great achievement.
May 1 : He set up Thomas Alva Edison Construction Department and upgraded central stations in USA.
June : Submitted 17 patent applications including some for electric lighting.
July 4 : At the opening of three wire ‘Edison Incandescent Electric Light’ at Central Station, Sunburry Pensylvania Edison registered his presence.
October 1 : Three wire underground central station system of Brocton, Massachuscttes became functional.
November 2 : A patent application in respect of electrical indicator was submitted. It was later known as ‘Edison effect lamp’ and was used by that very name.

1984
February 9 : A patent application for ‘Chemical Recording Stock Quotation Telegraph’ in association with Patrick Kenny submitted. It was registered as U.S. Patent No. 314115.
May 14 : Became Vice President of American Institute of Electrical Engineers. He also was its founder member.
Spring : After his return from Europe Charles Bachelor was made chief of Edison Machine Works.
August 9 : His wife Mary died in Menlo Park.
September 1 : Thomas A. Edison Construction Section was merged into Edison Company, that came up for lighting systems.
September 2 : Took part in International Electric Fair of Philadelphia.
October : Signed a contract with American Bell Telephone Company and the company agreed to pay Edison salary and expanses for experiments in respect of telephone.
1885
February 28 : Attended ‘World Industrial Millenium Fair’ organised in New Orleans.
April-May : Seventeen patent applications for telegraph and telephone related inventions were submitted.
June-July : Spent some weeks at Boston ‘Beach House’ of Ezra Gilliland. There he saw Mina Miller for the first time and started keeping a personal diary.
September 24-30 : Proposed to Mina at Boston.
October-November : Forwarded five applications for patent rights including one for telegraph invention.
Mid December : Met the family of Mina Miller in Ohio.
1886
Mid January : Bought Glenmont house for residence in Lavellin Park, New Jersey.
February 24 : Wedded Mina Miller.
May 16-31 : Employees of Edison Machine Works went on strike.
Spring : Held talks to get Edison United Manufacturing Company also do sales works like the electric light companies of Edison were engaged in.
June 23 : Edison announced that the Edison Machine Works will again be instituted in MacQueen Locomotive Shop, New York.
October : Tested upgraded phonograph.
November : Laboratory was again shifted to Edison Lamp Works, New Jersey.
February-April : Recovered from pleurisy while staying at Fort Myres, Florida.
May 3 : As architect for West Orange lab H. Hudson Holly was contracted.
May 24 : Patent application for Pyromagnetic and Electric Generator submitted.
July 30 : Dismissed H. Hudson Holly from architectural assignment.
August : A factory hired in Bloomfield New Jersey for the production of phonograph.
September : Charles Bachelor inspected the export and establishment works of West Orange laboratory.
October 1 : Signed contracts with L. Briggs and William. W. Jacks about rights to produce and market Edison phonograph equipped dolls.
October 10 : Edison Phonograph Company was set up.
October 14 : Signed contract with George E. Gourad in respect of international distribution rights of phonograph.
October 28 : Ezra was appointed chief sales agent of Edison Phonograph Co.
Phonograph patents were transfered to Edison Phonograph company through 11,960 shares.
Early December : Work in West Orange lab began in earnest.
December : Arthyr Kenedy was added to West Orange laboratory to enable Arthur Kenelly carry on electric researches in Galvanometer Room.
1888
January 17 : Application for patent was sent for ‘Electroplating of Duplicating Phonograph cylinder Records’. It was decided to carry on the tests for a full decade for commercial production of gold plated records.
January : For the purpose of research and production detailed talks were held while setting up partnership with Henry Billard.
Reginaled A. F. joined West Orange Chemical lab. He was entrusted with the research on insulation of electric wires for making electric system more safe and user friendly.
January-February : The research on fibres of bamboo, grass and other kinds were retaken for their use in heated filament light. For this purpose Frank M. and Charles Herrington were sent to S. America and James Roulton to Asia.
April 2 : Chosen as resident member of the New York Science Academy.
April-May : Jessie Lippincot met Ezra several times to buy rights of the Edison phonograph.
May 3 : Edison phonograph workshop was set up.
May 31 : The second wife of Edison presented him their first child and the second daughter of Thomas A. Edison called Medellion.
Construction of Phonograph works factory began in West Orange.
May-August : It was claimed that within a few weeks perfect Phonograph would be in the market.
May October : A 24 hour research was undertaken to upgrade the phonograph and the cylinder.
July 14 : North American Phonograph company was set up.
July-December : Arthur E. Kenelly and Harold P. Brown tested Electrocution Chair (proposed for execution of convicts awarded death penalty) on dogs and other animals.
August 1 : A contract signed by Jessie Lippincot North American Phonograph Co. for distribution of phonograph.
August-September : Henry Bollard consulted to strengthen the business of Edison General Electric Company.
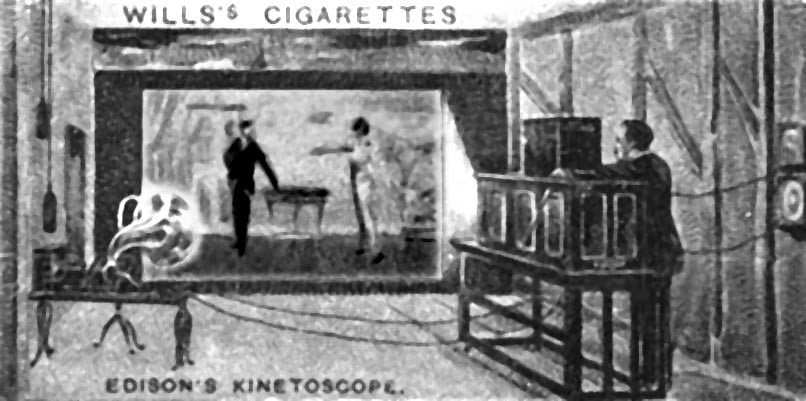
October 8 : Kinetoscope and Kinetograph related four main patent caveats were issued.
October-November : Small scale production of phonographs started in Phonograph Works of West Orange.
October-December : Research with chemicals carried out for the control of Yellow-Fever.
December 27 : Paid attention to set up branches in New Jersey and Pensylvania.
December 31 : Some unsuccessful experiments and test were put in ‘Dead experiments’ list. They included Synthetic silk, Typewriter, Cotton-Picker, Pyromagnetic Dynamo and Flying Machine.
1889
January 10-February 1 : Twelve patent applications forwarded in respect of phonograph and cylinder records.
January : Some cases of ‘Cheating and Fraud’ were filed against ex-associates like John C. Tom Leason and Ezra. The cheating had been done by violating the agreement terms with Jessie Lippincot and North American Phonograph Co.
March 6 : William J. Hammer was sent to 1889-Paris Expo as representative of the inventions of Thomas A. Edison.
March-July : In respect of execution by ‘Electrocution’ appeared in the hearing to record a statement in ‘William Camler Vs Charles F. Dartson’ Case.
August 3 : Set out to tour Europe with wife Mina and Francis Uptron. Took part in Paris-Expo and visited France, Belgium and Germay.
October 6 : Returned to USA.
November 8 : Pickskill tour and surveyed some iron ore mines of New York region.
December : Set up Edison Manufacturing Co. which was not incorporated.
1890
February 24 : Established ‘Edison United Phonograph Company’ with Edison as Vice President.
February : Set up Automatic Phonograph Exhibition Company to prepare distribution market for ‘Coin-in-the-slot-Phonograph’.
February-March : Toured Virginia and North Carolina to prospect ore reserves.
April 30 : Shut down experimental Ore Plant of Pensylvania.
Experiments on insulation in chemical lab were terminated and the staff was discharged.
May : The production of Talking Dolls by the Edison Phonograph works was suspended.
May-August : A long time continuous tests started at Augden mines, Sussex County of New Jersey for ore separation.
June 10 : In ‘Edison Electric Light Co. Vs U.S. Electric Lighting Co.’ case cross-examinations were completed.
Spring : After A.C. tests at Edison General Electric Co. plant, transformer was made in association with Arther E. Kenedy.
August 3 : Third son Charles was born to Edison.
August : Land purchased at Silver Lane, New Jersey for the plant, of ‘Edison Manufacturing Company.’
Street car motor related tests were carried out at ‘Edison General Electric Company’ plant.
September : Started ‘Science Fiction’ project with George P. Lethorpe.
October : Met failure in gaining control of Edison Phonograph Toy Manufacturing Company.
Signed Cooperation agreement with Edison General Electric Co. for research in electric light and energy.
December 3 : The factory of ‘Edison Iron concentrating Company’ Michigan caught fire.
1891
January : Jonasse W. Islesworth resigned from West Orange laboratory. Became advisor to workers for organising phonograph records works, speeded up work on X-Ray device and worked on heating lamp, in that serial order.
Edison reached Port Heuren to take part in the last rites of his elder brother William Pitt.
February : Visited the plant of Edison General Electric Company to inspect the progress of work on A.C. transformer and Street car.
May 12 : Reached Chicago to discuss matters related to 1893-Columbia Exhibition and electric lighting business.

May 20 : Gave demonstration of kinetoscope in West Orange lab before members of the women groups and organisations.
May 21 : New Jersey and Pensylvania area directors were authorised to buy Augden Iron Company.
May-June : New Jersey and Pensilvania concentrating works contracted Bethleham Iron Company for the supply of iron ore.
June-December : Edison spent most of his time at Augden plant of Concentrating Works.
July 14 : Edison’s main lamp patent was approved as the verdict in Edison Electric light Co. Vs U.S. Electric Lighting Company legal battle.
August 24 : Patent applications for kinetoscope and kinetograph were submitted.
1892
March : Tests on Iron ore bicketts carried out to see viability in respect of production and organisational aspects plus coordination.
April 15 : General Electric Co. reorganised.
Samuel Insel resigned from the posts with General Electric Co. and Phonograph works. He took charge of Edison Illuminating Company of Chicago.
June-July : Augden Plant village was renamed ‘Edison’ in his honour.
October : Agreement signed with General Electric Co. for cooperation in research in the fields of electric light and energy.
1893
February : Black Maria theatre construction was completed but decoration and furnishing work was yet to be done. The studio was rescheduled to open in May.

The matter of gaining contract for Niagra Falls Power Project was discussed with Arther E. Kennely in respect of cost and planning.
May 9 : Keyhole kinetoscope was exhibited at Brooklyn Institute of Arts and Sciences.
August-September : Went to Chicago with Miller family to take part in Columbia Expo.
December 29 : Patent application forwarded for ‘Joint & Crushing Rolls’.
The sensor employees were retrenched and several activities of laboratory curtailed.
Still spent most of his time at Augden plant. He was avaialbe at West Orange lab only on the weekends or Mondays.
Stocks of General Electric Company were sold.
1894
January 9 : Relinquished the post of the President of North American Phonograph Co. and vice presidentship of Edison United Phonograph Co.
January : William K.L. Dickson presented ‘Edison Kintographic Record of a Sneeze’. The copyright of the first motion picture was awarded. In 1894 Dickson and Theodor gained copyrights over 75 motion pictures.

March 1 : Arther E. Kennely relinquished his West Orange laboratory post and started his own consulting firm with a partner called Edwin H.
March : The first production contract for 25 Kinetoscopes was accomplished.
April 1 : William E. Gilmour took over management charge and vice presidentship of Edison Manufacturing Company.
April 14 : Holland brothers gave commercial demonstration of Peephole Kinetoscope at 1155, Broadway, New York city.
April : Private secretary of Edison resigned.
August 21 : Receiver was appointed on North American Phonograph Company. Newark Attorney John. R. Hardin was the receiver.
October 17 : First kinetoscope parlour opened in London, England.
December : Augden plant was temporarily shut down for repairs and modernisation.
1895
Edison spent most of his time at Augden plant.
Continued to sell bonds of Railroad and General Electric Co. staff groups.
April : William K.L. Dickson relinquished his West Orange laboratory post.
Summer : Extensive experiments carried out on iron ore to get desired quality for shipping and blast furnaces. The efforts continued till 1897.
October 1 : Daughter Marian E. Edison got married to Oscar A. at Dresden, Germany.
New contracts signed with General Electric Company for research and upgradation in electric lighting.
October 18 : Edison Electric Co. New York rejected Edison’s demand of $ 1 lakh he was to get at the business proving successful according to a 1885 contract term.
Development of cellular filament lamp with light current was again revived.
1896
January 15 : Primary contract signed with Thomas Ornett according to which Edison Manufacturing Co. was to produce ‘Ornett’s Fantoscope’ that worked like Edison’s Vitascope.
January 27 : National Phonograph Co. set up.
X-Ray experiments started.
February 26 : Edison’s father Samuel died in Ohio. He attended the funeral.
March : Fluaroscope of X-Ray was sent to Michael Pupin, physics scientist of Columbia University.
March-July : Augden plant again closed for modernisation.
April 23 : Edison Vitascope introduced to market through inauguration at ‘Coaster and Balls Music Hall’ New York city.
Samples of ‘Gold Ore Separation Process’ result sent to New Mexico mines.
May-July : Vitascope exhibited abroad.
Mid August : A grand convention of the group of Edison illuminating companies was held at Brooklyn, New York which was attended by Edison and Henry Ford.
November : In Edison Home Phonograph a cheaper version of the device was invented which operated on spring motor.
1897
Spent most of his time at concentrating works plant, Augden.
June : New Mexico gold sample received. Edison gold ore separation process was tested with it and cost of operation assessed.
July 16 : Invented high capacity Three Roller Ore Milling Process. Patent was applied for it.
August : As representative of Edison Manufacturing company James H. Watt sailed on a ten month international tour to scout for the subjects for motion pictures. 130 plus subjects were registered for copyright purpose.
November 30 : Edison’s own Projectoscope and Projecting Kinetoscope were tested as his first commercial inventions.
December : Edison filed several suits against his rivals for violations of patent rights. They included International Film Co., M & B Limited, American Mutoscope, Benjaminu P. Keith and Sigmund Lubin.
1898
Shuttled between West Orange lab and Augden.
July 8 : Mina Miller’s brother Theodor died fatally wounded in Spanish-American war.
July 10 : Fourth son was born to Edison. He was named after Mina’s dead brother namely ‘Theodor Edison’.
December 20 : Augden Pre-milling plant again shut down for repairs. Quarters for workers began to be constructed. In spring the plant reopened.
December : Went to see ‘Portland Cement’ plants in Pensylvania valley zone.
1899
January : Designed a long rotary furnace for cement manufacture.
February 17 : Edison’s father-in-law, Levis Miller died. Attended his funeral at Ohio.
February 22 : His long time associate John Crusoe passed away.
March 14 : Signed contract with Thomas Kraham of Clondyke Exposition Co. to aquire Motion Pictures of the Alaska Gold Field.
March : Constructed building for his long rotary furnace.
April 15 : Set up Edison Portland Cement Co.
May-June : Started experiments and test on storage batteries. A cement workshop was built at his facility.
1900
January 31 : Sister Marion passed away.
June 16 : Patent applied for in respect of the ‘Mass producing Cylinder Phonograph Records’.
August : Constructed a complete shape long furnace to produce cement at West Orange lab. Later it was shifted to Portland Cement Works situated at Stiburstville, New Jersey.
Summer : Edison’s testing and mixing mill related to gold ore was tested at Ortige mines.
September : Concentrating works of New Jersey and Pensylvania were postponed in view of the weak demand for iron in the market.
November 1 : Testing mill at Ortige mines was closed and poor quality ore was held responsible for the failure.
1901
Inspected under construction Edison Portland Cement Co. Works in New Jersey.
February 15 : Authorised Herman E. Dick to go abroad to negotiate setting up of companies there to manufacture storage batteries and their sale-cum-distribution.
Worked to open a motion pictures studio at 41, East 21 street, Manhattan.
Holidayed with family at Fort Myres, Florida. After 1887 went to see his winter lodge for the first time. He holidayed several winters at Fort Myre.
May 14 : Threatened with the abduction of his son and a ransom of gold worth $ 25,000 was demanded. Edison foiled the bid with the help of private detectives.
May 27 : Set up Edison Storage Batteries Co.
June : Advertised in Ore Journal to find a dry mine for his gold ore separation process.
July 17 : Gave Edison Storage Batteries Co. $ 10 lakh incorporated stock in $ 9,99,000.
1902
January : Presented moulded records commercially for trade.
April 25 : Edison Ore Milling Syndicate Ltd. set up ‘Dunderland Mine Ore Company Ltd’ to get benefit of Edison Ore Processing technique in Norway.
May 2 : Set up ‘Mining Exploration Co. as an incorporated body to get supplies of nickel for the storage batteries.
May 5 : Lord Kelvin visited New Orange lab.
May : Electric vehicles with Edison storage batteries were successfully tested on the roads.
August : Edison’s cement mill began the commercial production.
October 23 : Became technical advisor (nominally) of Marconi Wireless Telegraphy Company of America and Patent No. 465971 acquired for the company.
December 6 : Thomas A. Edison sold the rights of his name to Thomas A. Edison Junior Chemical Company that gained the patent of a medical instrument called ‘Magnoelectric Vitaliser’.
1903
January : ‘E’ type alkaline storage battery production began.
March 2 : Coal grinding plant of Edison Portland Cement Co. was wrecked by a blast killing 8 workers including chief engineer.
June 8 : Signed a contract with his son of the same name Thomas A. Edison Junior and according to it the son was not to use his name in any of his business for which he was to receive $ 35 a weak stipend.
September-October : New papers played up the stories of dissatisfaction and anger of the workers of some of the enterprises of Edison.
November 24 : Edison’s Attorney passed away soon after Legal Department was set up and Frank A. Dyre was appointed General Counsellor to safeguard the interests of Edison’s laboratory and his companies legally.
December 10 : Informed President Roosevelt about this decision of the Patent Office regarding storage batteries. Besides Edison a Swedish man Valdemar Junger had also applied for the patent of the same. The patent was given to the Swede. At last the patent of Valdemar was held null and void.
December : Edison Manufacturing Co. exhibited a hit movie The Great Train Robbery directed by Edvin A. Porter.
1904
February 10 : A non-American Chemist Martin was dismissed on 2nd February. Edison issued a declaration, ‘He was the last alien chemist he ever would contract. Now on I will give priority to young talented Americans only’.
April : Edison Manufacturing Company’s ‘Crew Films’ arranged to exhibit Russo-Japanese war films in America.
September 30 : Sigmund Bergman was authorised to set up Storage Batteries Corporation in Germany and start production.
October 2 : A lab worker named C.M. Dolly died due to radiation because of being involved too much and too long in X-ray experiments.
November 1 : Production of alkaline storage batteries was suspended to investigate and study loss of electric capacity and saving of acid in containers.
January 23 : Operated upon for a big boil.
February : Because of storage battery work he could not go on Florida holiday.
March 7 : J.P. Morgan Junior joined Edison lab. Discussed upgraded storage battery and their production by companies set up in Europe.
May-June : Experiments started on nickel plating the perforation tubes of batteries to get positive results from electric wires. This series of experiments continued for a decade.
September : Correspondence was resorted to in a bid to find cobalt reserves abroad. Edison wanted to use cobalt in storage batteries. Even telegrams were sent to parties abroad in this respect.
1906
January 25 : 30 year old legal battle against Atlantic & Pacific Telegraph Company of J. Gould for violating rights of Edison’s Automatic Telegraph Co. at last came to an end with the verdict in favour of Edison but compensation was only of one Dollar. Edison appealed and in 1911 the verdict was reversed.
March 26 : Bought a farm in New Jersey for his namesake son. He was recuperating after getting treated for alcohalism in a sanitorium.
May : Toured North Carolina and southern states by car in search of cobalt reserves.
July 7 : His namesake son got married to Beatrice with whom he had been living under a false name.
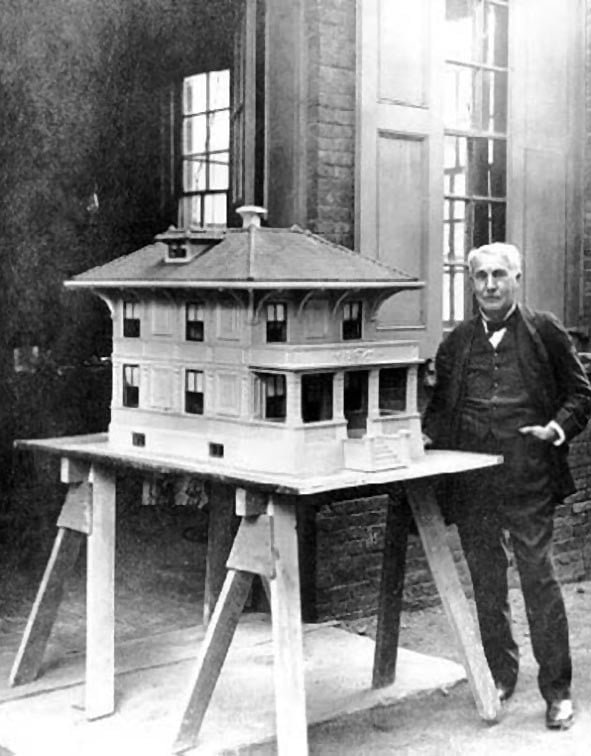
October : Considering a plan Edison declared building a house was possible with prefabricated cement concrete blocks.
1907
February 11 : He announced that he would soon disassociate himself from business activities and devote himself to laboratory like a scientist.
March 5 : U.S. Circuit Court penalised Edison with a fine for violating camera patent related limits to monopolise film production in U.S.A. He was held responsible for overstepping patent rights.
July : Motion Pictures production work was transferred to newly constructed studio in Bronx.
July 16 : National phonograph company opened a new office in New York city at 10 Fifth Avenue.
September 27 : Edison ordered closure of Durby Mines, Ontario, Canada. He had decided to keep his batteries cobaltless.
1908
January 8 : A supplementary licence contract was signed with North American Portland Cement Co. for cooperation in cement patents.
January 17 : Edison’s commercial phonographic company was incorporated.
February 17 : His private Secretary Randolf shot himself dead. Harry F. Miller was appointed in his place.
March : Charles L.B. was contracted to make Motion Pictures having colour photography.
July 23 : Frank L. Dyre replaced William E. Gilmour as C.E.O. of Edison firm.
September 1 : Acquired Lanceden Co. It used to make electric vehicles using Edison storage batteries.

October 1 : Introduced Amberoll cylinder records having 200 fibres or tissues or grooves. It enhanced record playtime by 2-4 minutes.
November 16 : Frank appointed a personal attendent for Edison to control his irritable nature and protect him from troublesome characters.
December : Under a contract Motion Picture Manufacturers was reorganised as ‘Motion Pictures Patent Co’.
1909
February : Edison agreed that if records with 400 fibres grooves were produced J.A. Islesworth and Walter H. Miller would get $ 25,000 and $ 10,000 respectively as bonus. Before this they too had earned bonuses of $ 35,000 and $ 10,000 for producing 200 groove records.
April : For invention of phonograph and thermal lamps Edison received Gold Medal from Royal Academy of Sciences, Sweden.
June : Shared his personal experiences with Thomas C. Martin to provide him material for his biography. The book came out in 1910 under the title His Life and Inventions The book was jointly prepared by Martin, Frank and William H.M.
July 1 : Commercial production of ‘A’ type alkaline storage batteries began.
November 10 : The director of Motion Pictures, Edvin S. Porter was dismissed.
1910
January 1 : Charles Bachelor passed away.
For the development of various enterprises of Edison an engineering wing was set up in New Orange laboratory for centralised research and development.
February 11 : J.W. Islesworth applied for patent of ‘Condensite’ which was made up of resin of Phenolic. Later it continued to be used in Edison’s disc records.
March : In New York city Edison’s storage batteries were used in street cars designed by S.H. Beech who was connected to Federal Storage Battery Car Co. He had sought the cooperation of Edison.

For upgradation of colour photography John H.P. and Florence M. Warner were brought to West Orange laboratory.
May : Some model residences and towns were exhibited in New York city. They were based on Edison’s concrete flow technique.
July 18 : Work plan upgraded with M.R. Huchinson to make storage batteries suitable for submarines.

August 26 : At West Orange lab talking movies and kinetograph were demonstrated before members of the press.
September 17 : Two electric vehicles powered by Edison batteries rolled out for New York for an inspirational voyage and it terminated at Mount Washington, New Hampshire.
October : Edison issued an unconventional statement to press and attracted nationwide attention. He made his views clear on immortal soul.
November : Gave a donation of $ 25 to the memory of the writer Isle-Adams who in his 1886 fiction ‘Eve Future’ included fictional Edison.
1911
About his statement on the immortality of the soul he expressed his reactions in Columbia magazine.
February 28 : Reorganised National Phonograph Co. as ‘Thomas A. Edison Incorporation’.
July 18 : Applied for patent for concrete furniture which was withdrawn later.
August-September : Toured Europe with Mina, her children Charles, Medellian and Theodor.
November 11 : Appointed Rees Miller as his personal representative at West Orange laboratory.
December 30 : Applied successfully for low capacity storage battery. This transportable battery was very useful in carry lamps, and safety lamps of mines.
1912
March 20 : Applied for patent of motor starter and battery. Patent right was granted.
August 12 : Appointed R. Miller his chief engineer and Bliss was removed from West Orange lab.
August 16 : Justice Department of U.S.A. moved against Motion Pictures Patent Co. of Edison.
September 16 : Campaign was started to produce disc records at big scale. Six workers were drafted for it who worked relentlessly to get the name ‘Insomnia Squad’.
September 19 : Edison supported Theodor Roosevelt for the presidential election and he also stood for voting rights for women.
October 7 : Blue Amberoll cylinder machines and records were shipped to get them to distributors of phonograph.
In Boston Electric Exhibition disc phonograph was demonstrated. They were distributed and sold all over USA with great zeal by the end of the year.
November 7 : Edison became President of the Thomas A. Edison Corporation replacing Frank Dyre. He retained the post till 1926.
November 29 : Contracted Henry Ford for a loan of $ 5 lakhs to set up a new factory to produce storage batteries for Ford Automobiles. In the next 2½ years Ford advanced loans totalling $ 12 lakh.
November : Began distribution of domestic projecting kinestoscope.
1913
January 23 : American Museum awarded Edison Retheno Medal for his sparkles batteries, battery lamps for mines and other useful inventions.

February 17 : In his presence kinetoscope was demonstrated in New York city theatre. In the following months the people enjoyed and admired ‘Talking Movies’.
May : In a survey conducted by Independent magazine Edison was chosen as the ‘Most Useful Person of America’.
1914
February 23-April 17 : Holidayed in Florida with Henry Ford family. They also undertook a water adventure voyage.
May 12 : Henry Ford inspired Edison against smoking Edison banned smoking in all his plants but he himself continued to smoke cigars and chewing tobacco. Meanwhile tobacco lobby continued to propagate the benefits of smoking.
September 8 : After the end of the war in Europe Edison announced he would set up plants to produce phenol and other chemicals that were much in demand. Five plants were set up but only are remained with Edison as incorporated body.
November : A commercial announcement was made to coordinate telephone and phonograph. It was made possible to record a telephonic talk at both ends.
December 9 : Fire destroyed half the building of West Orange laboratory. The fire started in the film inspection wing with an explosion.
1915
March 1 : Edison Corporation drafted departmental policies. S.B. Memburt was made incharge of engineering to implement those policies.
July 7 : American Navy appointed Edison the chairman of Naval Advisory Board.
August 9 : National level ‘Tune Test’ was held. Recording artists sang in disguise on the stage in the darkness. The audience were challenged to identify the singer. It was ‘Edison Diamond Disc Recording’ event. The recording was done for real.
October 14 : ‘Panama Pacific International Show’ was organised at San Francisco in honour of Edison. He attended along with his wife Mina, Henry Ford and met Luther Burbank. Visited Los Angeles and San Diego on the way.
1916
January 15 : Inspected E-2 submarine of U.S. Navy in Brooklyn Navy Yard that had suffered some blast. Five people died and ten injured gravely. Edison held hydrogen gas responsible for the blast. After that submarines used Edison batteries.
March 3 : The directors of Thomas Edison Incorporated chose S.B. Membert as Vice president and financial executive. Secretary treasurer and assistant manager resigned.
March 15 : Edison had to explain expenses of
1.5 million incurred on Naval researches.
June 12 : Charles Edison was chosen as the Chairman of Thomas Edison Incorporated and later he assumed chairmanship of Edison Storage Co. as well.
August 28 : Went on a adventure tour of the hills with Harvey Firestone and John. They were later joined by Henry Ford.
1917
February 8 : The months before U.S.A. joined the World War I Edison was devoting his entire time in doing experiments for the government and a lab had been set up on Eagle Rock Mount, West Orange. For the next 2 years mulled over patenting 16 inventions.
April 9 : U.S. Supreme court gave verdict against Edison in a motion pictures patent case. And a related contract was also held illegal. It was a legal set back.
April 21 : On an island conducted accoustic experiments for 6 weaks.
October 9 : Went to Washington D.C. to set up office in Naval Department. Did some useful research work. Sometime Admiral George Divey used to sit in that place.
1918
January 28 : Went to Key-West with Mina and stayed at the residence provided by the Navy. Did research work for Navy till the end of April.
March 30 : Winded up his motion pictures ventures. Sold his Bronx studio to a film company. The property was again acquired and resold when the first buyer went broke.
July 6 : Miller Rees, the Chief engineer of the lab resigned. John P. Constable took his place. He was a friend and M.I.T. mate of Charles Edison.
August 16 : Again went for adventure trip to Shanondoh valley and Great Smoky Mountains with H. Firestone, J. Brogan and H. Ford for two weeks.
1919
January 2 : When C.H. Wilson resigned from vice presidentship of Thomas A. Edison Incorporated, Charles took over that post and that of general manager as well.
April 11 : Openly supported President W. Wilson in organising U.N.O.
August 3 : Again went on a adventure trip with the same old company of tycoons.
September 15 : A campaign launched for starter batteries for the automobiles of Ford.
November 13 : Sent to Navy the last and final bill for his research and experimentation services. There stopped his military research works.

1920
October : The post-war recession forced Edison to streamline his companies. A lot of lay offs, retrenchments and dismissals took place affecting officials and workers alike.
1921
January 25 : Resigned from the membership of Naval Advisory Committee. At that time naval research laboratory and its objectives were under question.
July : Again went on an adventure tour.
1922
May : Proposed a policy for reforming the currency system. There was suggestion of loan to farmers based on cash worth of their crops.June : Rhutgurt University conferred a Honorary Doctorate of Sciences on Thomas A. Edison.
1923
August 1 : Attended the funeral of Warren E. Harding, the president of his Incorporation along with Henry Ford and Harvey Firestone. Holidayed in Canada with his wife Mina. Spent a month with Ford family at Detroit.

1924
August 28 : Edison Phonograph Works was merged into Thomas A. Edison Incorporation.
1926
February 1 : Sold all his patents to Thomas A. Edison Incorporation for $ 78,200.59 in cash.
August 2 : Resigned from the presidentship of Thomas A. Edison Inc. in favour of his son Charles.
October 26 : Presented long play disc records to help his phonograph business and upgraded the records to beat the compititors.
1927
July : Set up a Botanical Research Corporation to identify local plants of American environment that could help in rubber production.
1928
April : Radio industry was included in the company control at suggestion of Charles inspite of his own unwillingness. Splitdorf Bethlehem Company was acquired.
October 28 : A special community medal was awarded to Edison for contributing to the development and forward march of the society with his revolutionary inventions effecting the unprecedented social change and for being the most useful American citizen of the millenium. The medal was presented in a ceremony that was broadcast live and heard by 3,00,00,000 listeners.
1929
February 11 : Celebrated his 82nd birthday at Fort Myres with President Herbert Hoover, Henry Ford and Harvey Firestone.
July 28 : 49 last hopefuls took part in the compitition to get 1st Edison Scholarship. It was won by Wilber B. Huston, the son of Bishop of Seattle.
October 24 : Attended the inauguration and dedication functions of Greenfield village and Henry Ford Museum. The golden jubilee of the filament lamp/bulb was attended by the President Hoover and five hundred distinguished invitees. It was glorious ceremony.
October 26 : Stopped production of phonograph records and production was shifted towards radio from phonograph.
1931
January 6 : Applied for his last patent.
October 18 : Died in his Glenmont residence.
The above facts prove that Thomas Alva Edison was the first inventor who succeeded in giving practical shape to his scientific ideas and visualisation. His mind was multi-dimensional . He was capable of visualising new systems, thinking inventively, researching, upgrading, reforming, learning, improving, developing and giving his ideas commercially viable and profitable shape.

We can see a lot of special qualities in Edison’s character. His concepts were practicable and he by habit researched on a concept, refined and upgraded it and he could make his inventions sell and earn him rewards at commercial level. He never depended on the cash prizes, awards or doles or grants. To support his methodology and pride he created his own laboratory, workshop, machine shop organisation, production units, sales and distribution networks, factoris, offices and other facilities. For him inventions were his business. He was very careful about his rights and interests. Every concept, idea or invention he got immediately patented. And patent was milked in various ways commercially.
Setting up an industrial research lab by a scientist was an unprecedented thing. Upto the advent of Edison the researchers or the scientists used to work in laboratories and workshops of others renderings themselves very vulnerable for exploitations. The scientists used to sell their inventions to industrialists or businessmen. They never thought of going into the production of their own invention. The prouction and marketing would naturally appear an impossible task for those who could not manage to raise their own lab. Edison was a different kind of scientist. He was an inventor and entrepreneur of his inventions as well.
Although even for Edison it was not easy to coordinate all the activities from inventing to distributing the end product. He had an incredible will power, determination, industriousness, business sense, awareness to his interests and rights and very remarkable management talent. Those were responsible for his incredible successes.
God helps those who help themselves. It proved true on Edison. As a boy he revealed his innate inventiveness. A visit to the railway station got his inventive mind thinking. The idea struck him to make use of the situation and scene he was observing for his benefit. So, he began to sell newspaper and toffees. Then he realised the passengers needed time table bulletins. He printed it for them as a 12 year old boy. It got him self confidence and did his initial research in various facilities, railways and telegraphic offices. Then, he had his own lab and workshop.
At his vast lab at West Orange and other research facilities including machine shop he made many inventive devices and earned multi-dimensional scientific successes. For 35 years he worked there and became ‘Magician of Menlo Park’. Out of his magic bag came telegraphic devices, printers, telephonic transmitters, phonograph recording technique, filament bulbs and lamps, motion picture camera, ore separator, storage batteries, peephole kinetograph, cement making process etc.
Edison came from a low middle class family, yet he earned pots of money through his inventive mind and enterprise. He won the confidence of investors and got the money for his research and experiments. After successful research he did not forget to patent it. He took the services of the people who were well versed in patent laws. Then he would meet industrialists and distributors who were agreable to handle his inventions produced at large scale. He associated with the investors or financers. If he saw bigger opportunity he would unhesitatingly align with a new partner. Edison knew well that there was no place for sentiments in the world of business. The business is done with mind, and emotions are strictly for the heart which should stay confined one’s private life. The trade and industry was a heartless world.
To get to the heights of success the past relationships serve as ladder rungs. Still with some associates Edison maintained life long relationship.
In Thomas A. Edison a great inventor existed and in that inventor a great enterpreneuer lived. In his name the number of so many patents are registered in USA and other countries that no other scientist comes anywhere near to him. In thousands they run into.
Even at the age of 84, ten months before his death he applied for his last patent. So conscious was he of his rights and importance of his inventive idea. Age did not matter for Edison. His invention was his brain child and like every child it must get a name, in its case its Patent Number.
The world will always remember Thomas Alva Edison who lighted up our world, who was extremely prolific inventor who nursed his invention to the final end product, ready for our use. He ever thought of refinement upgradation, innovation, betterment, development, improvement and thus, in his own way he was working for a better world with happier life. He will be remembered for his creativeness, industriousness, resourcefulness and alertness in patenting his inventive ideas. He truly was an enterprising scientist or an inventive enterpreneur, a rare combination of gifts and talents.

