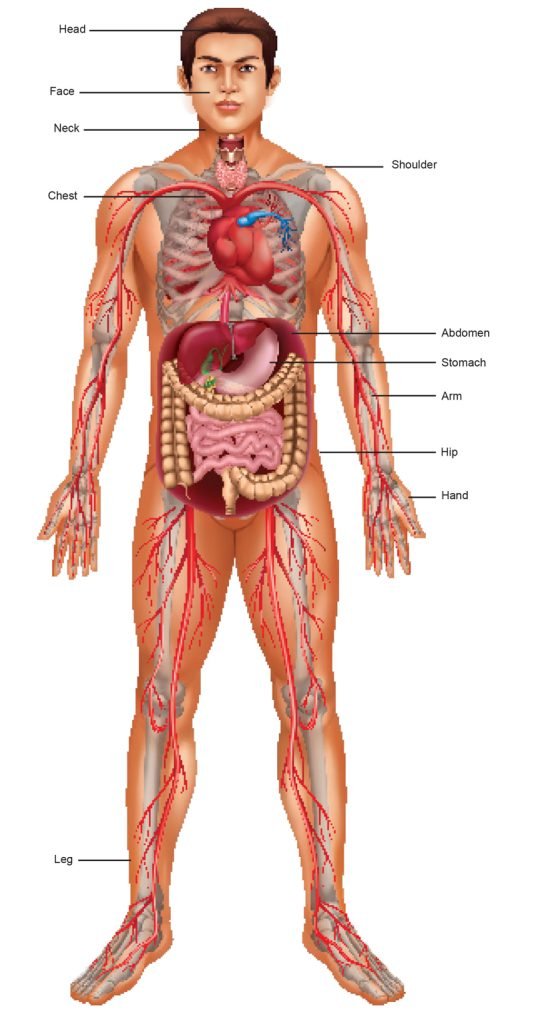
Head
The head includes the part of the body above the neck, principally the skull and the face along with the internal structures. The skull is the bony base of the head that protects the brain. When compared to the ancestors, the apes, human heads house big-sized brains. The size of a newborn baby’s head is about one-quarter of its entire body size, but at the time of adulthood, it remains only one-eighth of the entire body size. This is the reason why the newborns face difficulty in holding their heads.
Face
The face is the frontal part of the head. It is comprised of the forehead, the ears, the eyes with eyebrows, the cheeks, the nose, the jaw, the mouth, the lips and the chin. It is the highly sensitive region of the human body as it houses all the five sense organs. Our nose and ears keep growing throughout the life, but our eyes always remain the same in size. The facial muscles are one of the most delicate muscles, especially those present in the eyes and the lips.
Neck
The neck attaches the head to the rest of the body. Our neck is composed of different types of muscles. These muscles are responsible for the movement of the head. Apart from the movement of the head, these neck muscles contribute to the maintenance of blood flow to the brain, and they also assist in holding the head upright. The spinal cord begins from the neck. The part of the spinal cord in the neck is called the cervical spine.
Shoulder
The shoulder lies between the neck and the upper arm of the human body. It displays maximum mobility. The joints of the shoulders help the arms to rotate in a full circle as well as to elevate upward, downward, forward, backward and more. Shoulder movements help a gymnast to perform amazing stunts. But the excessive movement of shoulders while performing manual labour or exercise or sports, can break down the soft tissues in the shoulder region.
Chest
The part of the human body located between the neck and the abdomen is the chest. The chest is also called the thorax. The rib cage, spine and shoulder are also the part of the chest. The rib cage protects different organs underneath, including the heart, lungs and liver. The chest muscles support the movement of the shoulders. The chest muscles also play a part in breathing and pulling the rib cage to create room for the lungs to expand.
Arm and Hand :Human arm and hand are also referred as the upper limb. The shoulder, elbow, palm and the fingers are the part of the upper limb. The hand bones (carpals and metacarpals) and the muscles help us to hold things. The muscles in our fingers are so strong that only a few fingertips can bear the entire weight of the body while climbing vertical surfaces.
Abdomen
The part of the body that lies between the chest and the hip region is called the abdomen.
The digestive system is located in the abdomen. The stomach that is housed in the abdominal cavity can expand to hold up to 1.5 litres of food when full. Most of the movements in the body are supported by the back and the abdominal muscles, such as to sit, stand, bend over and pick things up.
Hip
The hip is the lowest part of the abdomen. It is in the pelvic region. The hip bone provides support to the body while sitting. The hip joint is the largest joint, crucial to support various postures of the body. The muscles in the hip facilitate the movement of the hip joint and also provide a natural cushion for the body. Among all the bones, the bones in the pelvic region are different in the males and the females. Females have more fragile pelvic bones than males.
Legs
Hip, thigh, knee, lower leg, ankle and foot together form a leg. The leg is a complex structure composed of several joints and muscles. The lower leg has two major bones and 20 different muscles that help in the movement of the leg and the toes. It is researched that the right leg is controlled by the left lobe of the brain and the left leg is controlled by the right lobe of the brain.